Cytotoxic CD4+ T lymphocytes may induce endothelial cell apoptosis in systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 31990684
- PMCID: PMC7190971
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI131700
Cytotoxic CD4+ T lymphocytes may induce endothelial cell apoptosis in systemic sclerosis
Abstract
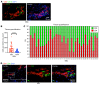
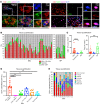
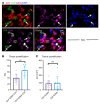
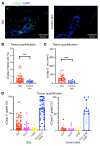
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is an autoimmune fibrotic disease whose pathogenesis is poorly understood and lacks effective therapies. We undertook quantitative analyses of T cell infiltrates in the skin of 35 untreated patients with early diffuse SSc and here show that CD4+ cytotoxic T cells and CD8+ T cells contribute prominently to these infiltrates. We also observed an accumulation of apoptotic cells in SSc tissues, suggesting that recurring cell death may contribute to tissue damage and remodeling in this fibrotic disease. HLA-DR-expressing endothelial cells were frequent targets of apoptosis in SSc, consistent with the prominent vasculopathy seen in patients with this disease. A circulating effector population of cytotoxic CD4+ T cells, which exhibited signatures of enhanced metabolic activity, was clonally expanded in patients with systemic sclerosis. These data suggest that cytotoxic T cells may induce the apoptotic death of endothelial and other cells in systemic sclerosis. Cell loss driven by immune cells may be followed by overly exuberant tissue repair processes that lead to fibrosis and tissue dysfunction.
Keywords: Autoimmune diseases; Autoimmunity; Fibrosis; Immunology; T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
T cells in SSc skin lesions: knowing your enemy.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020 May;16(5):253-254. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-0404-6. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32152550 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

