Phase I trial of donor-derived modified immune cell infusion in kidney transplantation
- PMID: 31990685
- PMCID: PMC7190926
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI133595
Phase I trial of donor-derived modified immune cell infusion in kidney transplantation
Abstract
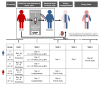
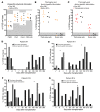
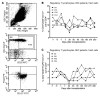
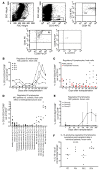
BACKGROUNDPreclinical experiments have shown that donor blood cells, modified in vitro by an alkylating agent (modified immune cells [MICs]), induced long-term specific immunosuppression against the allogeneic donor.METHODSIn this phase I trial, patients received either 1.5 × 106 MICs per kg BW on day -2 (n = 3, group A), or 1.5 × 108 MICs per kg BW on day -2 (n = 3, group B) or day -7 (n = 4, group C) before living donor kidney transplantation in addition to post-transplantation immunosuppression. The primary outcome measure was the frequency of adverse events (AEs) until day 30 (study phase) with follow-up out to day 360.RESULTSMIC infusions were extremely well tolerated. During the study phase, 10 treated patients experienced a total of 69 AEs that were unlikely to be related or not related to MIC infusion. No donor-specific human leukocyte antigen Abs or rejection episodes were noted, even though the patients received up to 1.3 × 1010 donor mononuclear cells before transplantation. Group C patients with low immunosuppression during follow-up showed no in vitro reactivity against stimulatory donor blood cells on day 360, whereas reactivity against third-party cells was still preserved. Frequencies of CD19+CD24hiCD38hi transitional B lymphocytes (Bregs) increased from a median of 6% before MIC infusion to 20% on day 180, which was 19- and 68-fold higher, respectively, than in 2 independent cohorts of transplanted controls. The majority of Bregs produced the immunosuppressive cytokine IL-10. MIC-treated patients showed the Immune Tolerance Network operational tolerance signature.CONCLUSIONMIC administration was safe and could be a future tool for the targeted induction of tolerogenic Bregs.TRIAL REGISTRATIONEudraCT number: 2014-002086-30; ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02560220.FUNDINGFederal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Technology, Berlin, Germany, and TolerogenixX GmbH, Heidelberg, Germany.
Keywords: Clinical Trials; Tolerance; Transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Moving from transplant as a treatment to transplant as a cure.J Clin Invest. 2020 May 1;130(5):2189-2191. doi: 10.1172/JCI136475. J Clin Invest. 2020. PMID: 32250338 Free PMC article.

