Crystal structure of PMGL2 esterase from the hormone-sensitive lipase family with GCSAG motif around the catalytic serine
- PMID: 31990908
- PMCID: PMC6986724
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226838
Crystal structure of PMGL2 esterase from the hormone-sensitive lipase family with GCSAG motif around the catalytic serine
Abstract
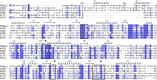
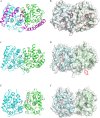
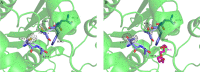
Lipases comprise a large class of hydrolytic enzymes which catalyze the cleavage of the ester bonds in triacylglycerols and find numerous biotechnological applications. Previously, we have cloned the gene coding for a novel esterase PMGL2 from a Siberian permafrost metagenomic DNA library. We have determined the 3D structure of PMGL2 which belongs to the hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) family and contains a new variant of the active site motif, GCSAG. Similar to many other HSLs, PMGL2 forms dimers in solution and in the crystal. Our results demonstrated that PMGL2 and structurally characterized members of the GTSAG motif subfamily possess a common dimerization interface that significantly differs from that of members of the GDSAG subfamily of known structure. Moreover, PMGL2 had a unique organization of the active site cavity with significantly different topology compared to the other lipolytic enzymes from the HSL family with known structure including the distinct orientation of the active site entrances within the dimer and about four times larger size of the active site cavity. To study the role of the cysteine residue in GCSAG motif of PMGL2, the catalytic properties and structure of its double C173T/C202S mutant were examined and found to be very similar to the wild type protein. The presence of the bound PEG molecule in the active site of the mutant form allowed for precise mapping of the amino acid residues forming the substrate cavity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
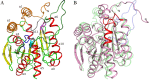

References
-
- Kumar L, Awasthi G, Singh B. Extremophiles: a novel source of industrially important enzymes. Biotechnology. 2011;10(2):121–35.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

