Late erythropoiesis-stimulating agents to prevent red blood cell transfusion in preterm or low birth weight infants
- PMID: 31990982
- PMCID: PMC6986694
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004868.pub6
Late erythropoiesis-stimulating agents to prevent red blood cell transfusion in preterm or low birth weight infants
Abstract
Background: Preterm infants have low plasma levels of erythropoietin (EPO), providing a rationale for the use of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) to prevent or treat anaemia. Darbepoetin (Darbe) and EPO are currently available ESAs.
Objectives: To assess the effectiveness and safety of late initiation of ESAs, between eight and 28 days after birth, in reducing the use of red blood cell (RBC) transfusions in preterm or low birth weight infants.
Search methods: We used the standard search strategy of Cochrane Neonatal to search the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL 2018, Issue 5), MEDLINE via PubMed (1966 to 5 June 2018), Embase (1980 to 5 June 2018), and CINAHL (1982 to 5 June 2018). We searched clinical trials databases, conference proceedings, and the reference lists of retrieved articles for randomised controlled trials and quasi-randomised trials.
Selection criteria: Randomised or quasi-randomised controlled trials of late initiation of EPO treatment (started at ≥ eight days of age) versus placebo or no intervention in preterm (< 37 weeks) or low birth weight (< 2500 grams) neonates.
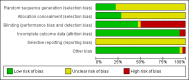
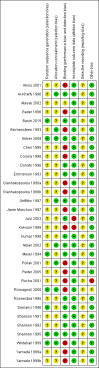
Data collection and analysis: We performed data collection and analyses in accordance with the methods of the Cochrane Neonatal Review Group. We used the GRADE approach to assess the quality of the evidence.
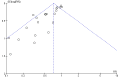
Main results: We include 31 studies (32 comparisons) randomising 1651 preterm infants. Literature searches in 2018 identified one new study for inclusion. No new on-going trials were identified and no studies used darbepoetin. Most included trials were of small sample size. The meta-analysis showed a significant effect on the use of one or more RBC transfusions (21 studies (n = 1202); typical risk ratio (RR) 0.72, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.65 to 0.79; typical risk difference (RD) -0.17, 95% CI -0.22 to -0.12; typical number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) 6, 95% CI 5 to 8). There was moderate heterogeneity for this outcome (RR I² = 66%; RD I² = 58%). The quality of the evidence was very low. We obtained similar results in secondary analyses based on different combinations of high/low doses of EPO and iron supplementation. There was no significant reduction in the total volume (mL/kg) of blood transfused per infant (typical mean difference (MD) -1.6 mL/kg, 95% CI -5.8 to 2.6); 5 studies, 197 infants). There was high heterogeneity for this outcome (I² = 92%). There was a significant reduction in the number of transfusions per infant (11 studies enrolling 817 infants; typical MD -0.22, 95% CI -0.38 to -0.06). There was high heterogeneity for this outcome (I² = 94%). Three studies including 404 infants reported on retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) (all stages or stage not reported), with a typical RR 1.27 (95% CI 0.99 to 1.64) and a typical RD of 0.09 (95% CI -0.00 to 0.18). There was high heterogeneity for this outcome for both RR (I² = 83%) and RD (I² = 82%). The quality of the evidence was very low.Three trials enrolling 442 infants reported on ROP (stage ≥ 3). The typical RR was 1.73 (95% CI 0.92 to 3.24) and the typical RD was 0.05 (95% CI -0.01 to 0.10). There was no heterogeneity for this outcome for RR (I² = 18%) but high heterogeneity for RD (I² = 79%). The quality of the evidence was very low.There were no significant differences in other clinical outcomes including mortality and necrotising enterocolitis. For the outcomes of mortality and necrotising enterocolitis, the quality of the evidence was moderate. Long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes were not reported.
Authors' conclusions: Late administration of EPO reduces the use of one or more RBC transfusions, the number of RBC transfusions per infant (< 1 transfusion per infant) but not the total volume (mL/kg) of RBCs transfused per infant. Any donor exposure is likely not avoided as most studies included infants who had received RBC transfusions prior to trial entry. Late EPO does not significantly reduce or increase any clinically important adverse outcomes except for a trend in increased risk for ROP. Further research of the use of late EPO treatment, to prevent donor exposure, is not indicated. Research efforts should focus on limiting donor exposure during the first few days of life in sick neonates, when RBC requirements are most likely to be required and cannot be prevented by late EPO treatment. The use of satellite packs (dividing one unit of donor blood into many smaller aliquots) may reduce donor exposure.
Copyright © 2020 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

Update of
-
Late erythropoiesis-stimulating agents to prevent red blood cell transfusion in preterm or low birth weight infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Feb 15;2(2):CD004868. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004868.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 28;1:CD004868. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004868.pub6. PMID: 30776084 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Akisu 2001 {published data only}
Al‐Kharfy 1996 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Kharfy T, Smyth JA, Wadsworth L, Krystal G, Fitzgerald C, Davis J, et al. Erythropoietin therapy in neonates at risk of having bronchopulmonary dysplasia and requiring multiple transfusions. Journal of Pediatrics 1996;129(1):89‐96. [PUBMED: 8757567] - PubMed
-
- Smyth JA, Ainsworth L, Krystal G, Wadsworth L. Effect of erythropoietin therapy on oxygen dependency in premature infants. Pediatric Research 2002;51(3):330 A.
Atasay 2002 {published data only}
-
- Atasay B, Gunlemez A, Akar N, Arsan S. Does early erythropoietin therapy decrease transfusions in anemia of prematurity?. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 2002;69(5):389‐91. [PUBMED: 12061670] - PubMed
Bader 1996 {published data only}
-
- Bader D, Blondheim O, Jonas R, Admoni O, Abend‐Winge M, Reich D, et al. Decreased ferritin levels, despite iron supplementation, during erythropoietin therapy in anaemia of prematurity. Acta Paediatrica 1996;85(4):496‐501. [PUBMED: 8740313] - PubMed
Basiri 2015 {published data only}
-
- Basiri B, Shokouhi M, Pezeshki N, Torabian S. Beneficial erythropoetic effects of recombinant human erythropoietin in very low‐birth weight infants: a single‐center randomized double‐blinded placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Neonatology 2015;4(2):87‐90. [DOI: 10.4103/2249-4847.154103] - DOI
Bechensteen 1993 {published data only}
-
- Bechensteen AG, Halvorsen S, Haga P. Erythropoiesis during rapid growth. Role of erythropoietin and nutrition. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1994;718:339‐40. [PUBMED: 8185241] - PubMed
-
- Bechensteen AG, Halvorsen S, Haga P, Cotes PM, Liestol K. Erythropoietin (Epo), protein and iron supplementation and the prevention of anaemia of prematurity: effects on serum immunoreactive Epo, growth and protein and iron metabolism. Acta Paediatrica 1996;85(4):490‐5. [PUBMED: 8346946] - PubMed
Bierer 2009 {published data only}
Chen 1995 {published data only}
Corona 1998 {published data only}
-
- Corona G, Fulia F, Liotta C, Barberi I. Clinical use of recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEPO) in the treatment of preterm anaemia [Uso clinico dell'eritropoietina umana ricombinante (rHuEPO) nell'anemia della prematurita]. Rivista Italiana Pediatria 1998;24:442‐9.
Donato 1996 {published data only}
-
- Donato H, Rendo P, Vivas R, Schvartzman G, Digregorio J, Vain N. Recombinant human erythropoietin in the treatment of anemia of prematurity: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial comparing three different doses. International Journal of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology 1996;3:279‐85.
Emmerson 1993 {published data only}
Giannakopoulou 1998a {published data only}
-
- Giannakopoulou C, Bolonaki I, Stiakaki E, Dimitriou H, Galanaki H, Hatzidaki E, et al. Erythropoietin (rHuEPO) administration to premature infants for the treatment of their anemia. Pediatric Hematology and Oncology 1998;15(1):37‐43. [PUBMED: 9509504] - PubMed
Giannakopoulou 1998b {published data only}
-
- Giannakopoulou C, Bolonaki I, Stiakaki E, Dimitriou H, Galanaki H, Hatzidaki E, et al. Erythropoietin (rHuEPO) administration to premature infants for the treatment of their anemia. Pediatric Hematology and Oncology 1998;15(1):37‐43. [PUBMED: 9509504] - PubMed
Griffiths 1997 {published data only}
-
- Griffiths G, Lall R, Chatfield S, Short A, MacKay P, Williamson P, et al. Randomised controlled double blind study of the role of recombinant erythropoietin in the prevention of chronic lung disease. Archives of Disease in Childhood. Fetal and Neonatal Edition 1997;76(3):F190‐2. [PUBMED: 9175950] - PMC - PubMed
Javier Manchon 1997 {published data only}
-
- Javier Manchon G, Natal Pujol A, Coroleu Lletget W, Zuasnabar Cotro A, Badia Barnusell J, Junca Piera J, et al. Randomized multi‐centre trial of the administration of erythropoietin in anemia of prematurity [Estudio multicentrico aleatorizado de administracion de eritropoyetina en la anemia de la prematuridad]. Anales Espanoles de Pediatria 1997;46(6):587‐92. [PUBMED: 9297428] - PubMed
Juul 2003 {published data only}
-
- Juul SE. Enterally dosed recombinant human erythropoietin does not stimulate erythropoiesis in neonates. Journal of Pediatrics 2003;143(3):321‐6. [PUBMED: 14517513] - PubMed
Kivivuori 1999 {published data only}
-
- Kivivuori SM, Virtanen M, Raivio KO, Viinikka L, Siimes MA. Oral iron is sufficient for erythropoietin treatment of very low birth‐weight infants. European Journal of Pediatrics 1999;158(2):147‐51. [PUBMED: 10048613] - PubMed
Kumar 1998 {published data only}
-
- Kumar P, Shankaran S, Krishnan RG. Recombinant human erythropoietin therapy for treatment of anemia of prematurity in very low birth weight infants: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of Perinatology 1998;18(3):173‐7. [PUBMED: 9659643] - PubMed
Maier 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Maier RF, Obladen M, Muller‐Hansen I, Kattner E, Merz U, Arlettaz R, et al. Early treatment with erythropoietin beta ameliorates anemia and reduces transfusion requirements in infants with birth weights below 1000 g. Journal of Pediatrics 2002;141(1):8‐15. [PUBMED: 12091844] - PubMed
Meyer 1994 {published data only}
-
- Meyer MP, Haworth C, McNeill L. Is the use of recombinant human erythropoietin in anemia of prematurity cost‐effective?. South African Medical Journal 1996;86(3):251‐3. [PUBMED: 8658295] - PubMed
-
- Meyer MP, Meyer JH, Commerford A, Hann FM, Sive AA, Moller G, et al. Recombinant human erythropoietin in the treatment of the anemia of prematurity: results of a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Pediatrics 1994;93(6 Pt 1):918‐23. [PUBMED: 8190577] - PubMed
Pollak 2001 {published data only}
-
- Pollak A, Hayde M, Hayn M, Herkner K, Lombard KA, Lubec G, et al. Effect of intravenous iron supplementation on erythropoiesis in erythropoietin‐treated premature infants. Pediatrics 2001;107(1):78‐85. [PUBMED: 11134438] - PubMed
Reiter 2005 {published data only}
-
- Reiter PD, Rosenberg AA, Valuck R, Novak K. Effect of short‐term erythropoietin therapy in anemic premature infants. Journal of Perinatology 2005;25(2):125‐9. [PUBMED: 15526012] - PubMed
Rocha 2001 {published data only}
-
- Rocha VL, Benjamin AC, Procianoy RS. The effect of recombinant human erythropoietin on the treatment of anemia of prematurity. Journal de Pediatria 2001;77(2):75‐83. [PUBMED: 14647595] - PubMed
Romagnoli 2000 {published data only}
-
- Romagnoli C, Zecca E, Gallini F, Girlando P, Zuppa AA. Do recombinant human erythropoitetin and iron supplementation increase the risk of retinopathy of prematurity?. European Journal of Pediatrics 2000;159(8):627‐8. [PUBMED: 10968244] - PubMed
Ronnestad 1995 {published data only}
-
- Ronnestad A, Moe PJ, Breivik N. Enhancement of erythropoiesis by erythropoietin, bovine protein and energy fortified mother's milk during anaemia of prematurity. Acta Paediatrica 1995;84(7):809‐11. [PUBMED: 7549303] - PubMed
Samanci 1996 {published data only}
Shannon 1991 {published data only}
-
- Newton NR, Leonard CH, Piecuch RE, Phibbs RH. Neurodevelopmental outcome of prematurely born children treated with recombinant erythropoietin in infancy. Journal of Perinatology 1999;19(6 Pt 1):403‐6. [PUBMED: 10685268] - PubMed
-
- Shannon KM, Mentzer WC, Abels RI, Freeman P, Newton N, Thompson D, et al. Recombinant human erythropoietin in the anemia of prematurity: results of a placebo‐controlled pilot study. Journal of Pediatrics 1991;118(6):949‐55. [PUBMED: 2040933] - PubMed
Shannon 1992 {published data only}
-
- Shannon KM, Mentzer WC, Abels RI, Wertz M, Thayer‐Moriyama J, Li WY, et al. Enhancement of erythropoiesis by recombinant human erythropoietin in low birth weight infants: a pilot study. Journal of Pediatrics 1992;120(4 Pt 1):586‐92. - PubMed
Shannon 1995 {published data only}
-
- Bard H, Widness JA. Effect of recombinant human erythropoietin on the switchover from fetal to adult hemoglobin synthesis in preterm infants. Journal of Pediatrics 1995;127(3):478‐80. [PUBMED: 7544827] - PubMed
-
- Brown MS, Shapiro H. Effect of protein intake on erythropoiesis during erythropoietin treatment of anemia of prematurity. Journal of Pediatrics 1996;128(4):512‐7. [PUBMED: 8618185] - PubMed
-
- Shannon KM, Keith JF 3rd, Mentzer WC, Ehrenkranz RA, Brown MS, Widness JA, et al. Recombinant human erythropoietin stimulates erythropoiesis and reduces erythrocyte transfusions in very low birth weight preterm infants. Pediatrics 1995;95(1):1‐8. [PUBMED: 7770284] - PubMed
Whitehall 1999 {published data only}
-
- Whitehall JS, Patole SK, Campbell P. Recombinant human erythropoietin in anemia of prematurity. Indian Pediatrics 1999;36(1):17‐27. [PUBMED: 10709119] - PubMed
Yamada 1999a {published data only}
-
- Yamada M, Takahashi R, Chiba Y, Ito T, Nakae N. Effects of recombinant human erythropoietin in infants with anemia of prematurity. I. Results in infants with birth weights between 1,000 and 1,499 gm. Acta Neonatologica Japonica 1999;35(4):755‐61.
Yamada 1999b {published data only}
-
- Yamada M, Takahashi R, Chiba Y, Ito T, Nakae N. Effects of recombinant human erythropoietin in infants with anemia of prematurity. II. Results in infants with birth weights between 500 and 999 gm. Acta Neonatologica Japonica 1999;35(4):762‐7.
References to studies excluded from this review
Ahmadpour Kacho 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ahmadpour Kacho M, Zahed Pasha YA, Esmaili MR, Hajian K, Moradi SH. The effect of human recombinant erythropoietin on prevention of anemia of prematurity. Pediatric Research 2003;54(4):564.
Amin 2004 {published data only}
-
- Amin AA, Alzahrani DM. Efficacy of erythropoietin in premature infants. Pediatric Research 2003;54(4):557. [PUBMED: 11938417]
Badiee 2006 {published data only}
-
- Badiee Z, Pourmirzaiee MA, Kelishadi R, Naseri F. Recombinant human erythropoietin and blood transfusion in low‐birth weight preterm infants under restrictive transfusion guidelines. Saudi Medical Journal 2006;27(6):817‐20. [PUBMED: 16758042] - PubMed
Bechensteen 1997 {published data only}
-
- Bechensteen AG, Hågå P, Halvorsen S, Liestøl K, Lindemann R, Whitelaw A, et al. Effect of low and moderate doses of recombinant human erythropoietin on the haematological response in premature infants on high protein and iron intake. European Journal of Pediatrics 1997;156(1):56‐61. [PUBMED: 9007493] - PubMed
Messer 1993 {published data only}
-
- Messer J, Haddad J, Donato L, Astruc D, Matis J. Early treatment of premature infants with recombinant human erythropoietin. Pediatrics 1993;92(4):519‐23. [PUBMED: 8414820] - PubMed
Meyer 1996 {published data only}
-
- Meyer MP, Haworth C, Meyer JH, Commerford A. A comparison of oral and intravenous iron supplementation in preterm infants receiving recombinant erythropoietin. Journal of Pediatrics 1996;129(2):258‐63. [PUBMED: 8765624] - PubMed
Mohammadzadeh 2005 {published data only}
-
- Mohammadzadeh A, Naseri F. Effect of high versus low doses of human recombinant erythropoietin on the anemia of prematurity. Acta Medica Iranica 2005;43(2):95‐8.
Ohls 1991 {published data only}
-
- Bierer R, Roohi M, Ohls RK. A randomized, masked study of weekly erythropoietin dosing in neonates. Pediatric Academic Societies' Annual Meeting. 2008:E‐PAS2008:633749.3.
-
- Ohls RK, Christensen RD. Recombinant erythropoietin compared with erythrocyte transfusion in the treatment of anemia of prematurity. Journal of Pediatrics 1991;119(5):781‐8. - PubMed
Ohls 2012 {published data only}
-
- Bierer R, Roohi M, Ohls RK. A randomized, masked study of weekly erythropoietin dosing in neonates. Pediatric Academic Societies' Annual Meeting. 2008:E‐PAS2008:633749.3.
Pasha 2008 {published data only}
-
- Pasha YZ, Ahmadpour‐Kacho M, Hajiahmadi M, Hosseini MB. Enteral erythropoietin increases plasma erythropoietin level in preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial. Indian Pediatrics 2008;45(1):25‐8. [PUBMED: 18250501] - PubMed
Pathak 2003 {published data only}
Testa 1998 {published data only}
-
- Testa M, Reali A, Copula M, Pinna B, Birocchi F, Pisu C, et al. Role of rHuEpo on blood transfusions in preterm infants after the fifteenth day of life. Pediatric Hematology and Oncology 1998;15(5):415‐20. [PUBMED: 9783307] - PubMed
Warwood 2005 {published data only}
Warwood 2011 {published data only}
-
- Warwood TL, Lambert DK, Henry E, Christensen RD. Very low birth weight infants qualifying for a 'late' erythrocyte transfusion: does giving darbepoetin along with the transfusion counteract the transfusion's erythropoietic suppression?. Journal of Perinatology 2011;31(Suppl 1):S17‐21. - PubMed
Widness 2006 {published data only}
-
- Widness JA, Serfass RE, Haiden N, Nelson SE, Lombard KA, Pollak A. Erythrocyte iron incorporation but not absorption is increased by intravenous iron administration in erythropoietin‐treated premature infants. Journal of Nutrition 2006;136(7):1868‐73. [DOI: 10.1093/jn/136.7.1868; PUBMED: 16772451] - DOI - PubMed
Additional references
Aher 2012b
Brown 1983
-
- Brown MS, Phibbs RH, Gracia JF, Dallman PR. Postnatal changes in erythropoietin levels in untransfused premature infants. Journal of Pediatrics 1983;103(4):612‐7. [PUBMED: 6194281] - PubMed
Cohen 1998
-
- Cohen A, Manno C. Transfusion practices in infants receiving assisted ventilation. Clinics in Perinatology 1998;25(1):97‐111. [PUBMED: 9523077] - PubMed
CONSORT 2012
Dallman 1981
Dame 2001
Egrie 2001
Finch 1982
-
- Finch CA. Erythropoiesis, erythropoietin and iron. Blood 1982;60:1241‐6. - PubMed
Garcia 2002
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
-
- GRADE Working Group, McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 5 June 2018. Hamilton (ON): GRADE Working Group, McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015.
Hesse 1997
-
- Hesse L, Eberl W, Schlaud M, Poets CF. Blood transfusion. Iron load and retinopathy of prematurity. European Journal of Pediatrics 1997;156(6):465‐70. [PUBMED: 9208245] - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2017
-
- Higgins JP, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2017. Available from training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Juul 2002
-
- Juul S. Erythropoietin in the central nervous system, and its use to prevent hypoxic‐ischemic brain damage. Acta Paediatrica 2002;91 Suppl(438):36‐42. [PUBMED: 12477263] - PubMed
Kotto‐Kome 2004
-
- Kotto‐Kome AC, Garcia MG, Calhoun DA, Christensen RD. Effect of beginning recombinant erythropoietin treatment within the first week of life among very‐low‐birth‐weight neonates, on "early" and "late" erythrocyte transfusions: a meta‐analysis. Journal of Perinatology 2004;24(1):24‐9. [DOI: 10.1038/sj.jp.7211018; PUBMED: 14726934] - DOI - PubMed
Lopez 2015
-
- Lopez E, Beuchée A, Truffert P, Pouvreau N, Patkai J, Baud O, et al. Recombinant human erythropoietin in neonates: guidelines for clinical practice from the French Society of Neonatology [L’érythropoïétine humaine recombinante chez le nouveau‐né : recommandations pour la pratique clinique de la Société française de néonatologie]. Archives de Pédiatrie 2015;22(10):1092‐7. [DOI: 10.1016/j.arcped.2015.07.001; PUBMED: 26320680] - DOI - PubMed
Ohls 2000
-
- Ohls RK. The use of erythropoietin in neonates. Clinics in Perinatology 2000;27(3):681‐96. [PUBMED: 10986635] - PubMed
Ohls 2002
-
- Ohls RK. Erythropoietin treatment in extremely low birth weight infants: blood in versus blood out. Journal of Pediatrics 2002;141(1):3‐6. - PubMed
Ohlsson 2012
Ohlsson 2017
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias: dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273(5):408‐12. [PUBMED: 7823387] - PubMed
Schünemann 2013
-
- Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A, editor(s). Handbook for grading the quality of evidence and the strength of recommendations using the GRADE approach (updated October 2013). gdt.guidelinedevelopment.org/app/handbook/handbook.html (accessed prior to 23 January 2019).
Stockman 1978
-
- Stockman JA 3rd, Oski FA. Physiological anaemia of infancy and the anaemia of prematurity. Clinics in Hematology 1978;7(1):3‐18. [PUBMED: 657601] - PubMed
Stockman 1986
-
- Stockman JA 3rd. Anemia of prematurity. Current concept in the issue of when to transfuse. Pediatric Clinics of North America 1986;33(1):111‐28. [PUBMED: 3513096] - PubMed
Strauss 1986
-
- Strauss RG. Current issues in neonatal transfusions. Vox Sanguinis 1986;51(1):1‐9. [PUBMED: 3526725] - PubMed
Vamvakas 2001
-
- Vamvakas EC, Strauss RG. Meta‐analysis of controlled clinical trials studying the efficacy of rHuEPO in reducing blood transfusions in the anemia of prematurity. Transfusion 2001;41(3):406‐15. [PUBMED: 11274599] - PubMed
Widness 1996
-
- Widness JA, Seward VJ, Kromer IJ, Burmeiser LF, Bell EF, Strauss RG. Changing patterns of red blood cell transfusion in very low birth weight infants. Journal of Pediatrics 1996;129(5):680‐7. [PUBMED: 8917234] - PubMed
Yu 2010
-
- Yu Z, Guo X, Han S, Lu J, Sun Q, Ohlsson A. Erythropoietin for term and late preterm infants with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008316] - DOI
References to other published versions of this review
Aher 2006b
Aher 2012a
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

