Inhibitory Activity of Flavonoids, Chrysoeriol and Luteolin-7- O-Glucopyranoside, on Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase from Capsicum chinense
- PMID: 31991570
- PMCID: PMC7072517
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10020180
Inhibitory Activity of Flavonoids, Chrysoeriol and Luteolin-7- O-Glucopyranoside, on Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase from Capsicum chinense
Abstract
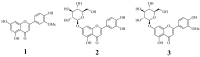
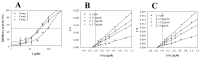
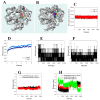
: Three flavonoids derived from the leaves of Capsicum chinense Jacq. were identified as chrysoeriol (1), luteolin-7-O-glucopyranoside (2), and isorhamnetin-7-O-glucopyranoside (3). They had IC50 values of 11.6±2.9, 14.4±1.5, and 42.7±3.5 µg/mL against soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH), respectively. The three inhibitors (1-3) were found to non-competitively bind into the allosteric site of the enzyme with Ki values of 10.5±3.2, 11.9 ±2.8 and 38.0±4.1 µg/mL, respectively. The potential inhibitors 1 and 2 were located at the left edge ofa U-tube shape that contained the enzyme active site. Additionally, we observed changes in several factors involved in the binding of these complexes under 300 K and 1 bar. Finally, it was confirmed that each inhibitor, 1 and 2, could be complexed with sEH by the "induced fit" and "lock-and-key" models.
Keywords: flavonoids; induced fit; lock-and-key; non-competitive mode; soluble epoxide hydrolase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

