Polygenic Risk Scores Shed Light on the Relationship between Schizophrenia and Cognitive Functioning: Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 31991840
- PMCID: PMC7074036
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9020341
Polygenic Risk Scores Shed Light on the Relationship between Schizophrenia and Cognitive Functioning: Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
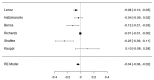
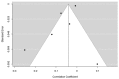
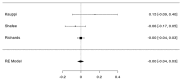
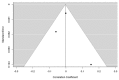
Schizophrenia is a multifactorial disease associated with widespread cognitive impairment. Although cognitive deficits are one of the factors most strongly associated with functional impairment in schizophrenia (SZ), current treatment strategies hardly tackle these impairments. To develop more efficient treatment strategies in patients, a better understanding of their pathogenesis is needed. Recent progress in genetics, driven by large genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and the use of polygenic risk scores (PRS), has provided new insights about the genetic architecture of complex human traits, including cognition and SZ. Here, we review the recent findings examining the genetic links between SZ and cognitive functions in population-based samples as well as in participants with SZ. The performed meta-analysis showed a negative correlation between the polygenetic risk score of schizophrenia and global cognition (p < 0.001) when the samples rely on general and healthy participants, while no significant correlation was detected when the three studies devoted to schizophrenia patients were meta-analysed (p > 0.05). Our review and meta-analysis therefore argues against universal pleiotropy for schizophrenia alleles and cognition, since cognition in SZ patients would be underpinned by the same genetic factors than in the general population, and substantially independent of common variant liability to the disorder.
Keywords: cognition; educational attainment; genetics; genome wide association study (GWAS); intelligence; polygenic risk score; schizophrenia.
Conflict of interest statement
P.G. received during the last 5 years fees for presentations at congresses or participation in scientific boards from Alcediag-Alcen, Angelini, GSK, Jansse, Lundbeck, Otsuka, SAGE and Servier. The other authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures
References
-
- Deary I.J., Weiss A., Batty G.D. Intelligence and Personality as Predictors of Illness and Death: How Researchers in Differential Psychology and Chronic Disease Epidemiology Are Collaborating to Understand and Address Health Inequalities. Psychol. Sci. Public Interest J. Am. Psychol. Soc. 2010;11:53–79. doi: 10.1177/1529100610387081. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gale C.R., Hatch S.L., Batty G.D., Deary I.J. Intelligence in childhood and risk of psychological distress in adulthood: The 1958 National Child Development Survey and the 1970 British Cohort Study. Intelligence. 2009;37:592–599. doi: 10.1016/j.intell.2008.09.002. - DOI
-
- Gale C.R., Batty G.D., Tynelius P., Deary I.J., Rasmussen F. Intelligence in early adulthood and subsequent hospitalisation and admission rates for the whole range of mental disorders: Longitudinal study of 1,049,663 men. Epidemiol. Camb. Mass. 2010;21:70–77. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181c17da8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

