Evaluation of the Burden of HPV-Related Hospitalizations as a Useful Tool to Increase Awareness: 2007-2017 Data from the Sicilian Hospital Discharge Records
- PMID: 31991909
- PMCID: PMC7157634
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines8010047
Evaluation of the Burden of HPV-Related Hospitalizations as a Useful Tool to Increase Awareness: 2007-2017 Data from the Sicilian Hospital Discharge Records
Abstract
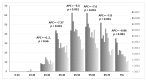
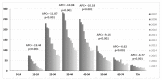
In light of the implementation of human papillomavirus (HPV) prevention strategies, epidemiological studies in different geographical areas are required in order to assess the impact of HPV-related diseases. The purpose of the present study was to describe the burden of HPV-related hospitalizations in Sicily. A retrospective observational study estimated 43,531 hospitalizations attributable to HPV from 2007 to 2017. During the observed period, there was a decrease for all HPV-related conditions with a higher reduction, among neoplasms, for cervical cancer (annual percent change (APC) = -9.9%, p < 0.001). The median age for cervical cancer was 45 years old, with an increasing value from 43 to 47 years (p < 0.001). The age classes with greater decreases in hospital admissions for invasive cancers were women aged 35 years or more (APC range from -5.5 to -9.86) and 25-34 years old (APC = -11.87, p < 0.001) for women with cervical carcinoma in situ. After ten years for vaccine introduction and sixteen years for cervical cancer screening availability, a relatively large decrease in hospital admissions for cervical cancer and other HPV-related diseases in Sicily was observed. Some clinical characteristics of hospitalization, such as increasing age, are suggestive clues for the impact of preventive strategies, but further research is needed to confirm this relationship.
Keywords: HPV vaccine; HPV-related disease; Italy; burden; cervical cancer; cervical cancer screening; hospitalization rate; impact evaluation; screening effectiveness; vaccine effectiveness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chauhan S.C., Jaggi M., Bell M.C., Verma M., Kumar D. Epidemiology of Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) in Cervical Mucosa. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009;471:439–456. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

