C-2 phenyl replacements to obtain potent quinoline-based Staphylococcus aureus NorA inhibitors
- PMID: 31992093
- PMCID: PMC7034129
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1719083
C-2 phenyl replacements to obtain potent quinoline-based Staphylococcus aureus NorA inhibitors
Abstract
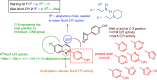
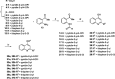
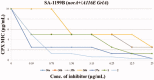
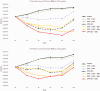
NorA is the most studied efflux pump of Staphylococcus aureus and is responsible for high level resistance towards fluoroquinolone drugs. Although along the years many NorA efflux pump inhibitors (EPIs) have been reported, poor information is available about structure-activity relationship (SAR) around their nuclei and reliability of data supported by robust assays proving NorA inhibition. In this regard, we focussed efforts on the 2-phenylquinoline as a promising chemotype to develop potent NorA EPIs. Herein, we report SAR studies about the introduction of different aryl moieties on the quinoline C-2 position. The new derivative 37a showed an improved EPI activity (16-fold) with respect to the starting hit 1. Moreover, compound 37a exhibited a high potential in time-kill curves when combined with ciprofloxacin against SA-1199B (norA+). Also, 37a exhibited poor non-specific effect on bacterial membrane polarisation and showed an improvement in terms of "selectivity index" in comparison to 1.
Keywords: Antimicrobial resistance breakers; NorA; Staphylococcus aureus; antimicrobial resistance; efflux pump inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
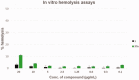
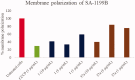

References
-
- Ten threats to global health in 2019. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/ten-threats-to-global-health-in-2019 [last accessed 7 Apr 2019].
-
- Piddock LJV. Understanding the basis of antibiotic resistance: a platform for drug discovery. Microbiology 2014;160:2366–73. - PubMed
-
- Wright GD. Antibiotic adjuvants: rescuing antibiotics from resistance. Trends Microbiol 2016;24:862–71. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
