Fluorescent amplification for next generation sequencing (FA-NGS) library preparation
- PMID: 31992180
- PMCID: PMC6988211
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-020-6481-8
Fluorescent amplification for next generation sequencing (FA-NGS) library preparation
Abstract
Background: Next generation sequencing (NGS) has become a universal practice in modern molecular biology. As the throughput of sequencing experiments increases, the preparation of conventional multiplexed libraries becomes more labor intensive. Conventional library preparation typically requires quality control (QC) testing for individual libraries such as amplification success evaluation and quantification, none of which occur until the end of the library preparation process.
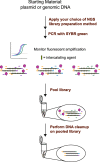
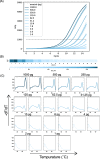
Results: In this study, we address the need for a more streamlined high-throughput NGS workflow by tethering real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) to conventional workflows to save time and implement single tube and single reagent QC. We modified two distinct library preparation workflows by replacing PCR and quantification with qPCR using SYBR Green I. qPCR enabled individual library quantification for pooling in a single tube without the need for additional reagents. Additionally, a melting curve analysis was implemented as an intermediate QC test to confirm successful amplification. Sequencing analysis showed comparable percent reads for each indexed library, demonstrating that pooling calculations based on qPCR allow for an even representation of sequencing reads. To aid the modified workflow, a software toolkit was developed and used to generate pooling instructions and analyze qPCR and melting curve data.
Conclusions: We successfully applied fluorescent amplification for next generation sequencing (FA-NGS) library preparation to both plasmids and bacterial genomes. As a result of using qPCR for quantification and proceeding directly to library pooling, the modified library preparation workflow has fewer overall steps. Therefore, we speculate that the FA-NGS workflow has less risk of user error. The melting curve analysis provides the necessary QC test to identify and troubleshoot library failures prior to sequencing. While this study demonstrates the value of FA-NGS for plasmid or gDNA libraries, we speculate that its versatility could lead to successful application across other library types.
Keywords: Echo; High-throughput; Library preparation; NGS; Next generation sequencing; SYBR green; qPCR.
Conflict of interest statement
NJH declares financial interests in TeselaGen Biotechnologies and Ansa Biotechnologies. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development of a robust DNA quality and quantity assessment qPCR assay for targeted next-generation sequencing library preparation.Int J Oncol. 2016 Oct;49(4):1755-65. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3654. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27511764 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and Easy Protocol for Quantification of Next-Generation Sequencing Libraries.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1735:343-350. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7614-0_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29380326
-
AG-NGS: a powerful and user-friendly computing application for the semi-automated preparation of next-generation sequencing libraries using open liquid handling platforms.Biotechniques. 2014 Jan;56(1):28-35. doi: 10.2144/000114124. Biotechniques. 2014. PMID: 24447136
-
Library preparation methods for next-generation sequencing: tone down the bias.Exp Cell Res. 2014 Mar 10;322(1):12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.01.008. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Exp Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24440557 Review.
-
Rapid quantification of DNA libraries for next-generation sequencing.Methods. 2010 Apr;50(4):S15-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2010.01.004. Methods. 2010. PMID: 20215015 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-Cell Sequencing in Rheumatic Diseases: New Insights from the Perspective of the Cell Type.Aging Dis. 2022 Dec 1;13(6):1633-1651. doi: 10.14336/AD.2022.0323. eCollection 2022 Dec 1. Aging Dis. 2022. PMID: 36465169 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, robust plasmid verification by de novo assembly of short sequencing reads.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Oct 9;48(18):e106. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa727. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32890398 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging the fundamentals of heat transfer and fluid mechanics in microscale geometries for automated next-generation sequencing library preparation.Sci Rep. 2024 May 31;14(1):12564. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63014-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38822053 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

