Use of a rapid recombinase-aided amplification assay for Mycoplasma pneumoniae detection
- PMID: 31992210
- PMCID: PMC6988361
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-019-4750-4
Use of a rapid recombinase-aided amplification assay for Mycoplasma pneumoniae detection
Abstract
Background: Mycoplasma pneumoniae is one of the most common causative pathogens of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), accounting for as many as 30-50% of CAP during peak years. An early and rapid diagnostic method is key for guiding clinicians in their choice of antibiotics.
Methods: The recombinase-aided amplification (RAA) assay is a recently developed, rapid detection method that has been used for the detection of several pathogens. The assays were performed in a one-step single tube reaction at 39° Celsius within 15-30 min. In this study, we established an RAA assay for M. pneumoniae using clinical specimens for validation and commercial real-time PCR as the reference method.
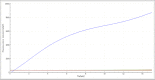
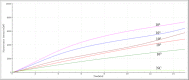
Results: The analytical sensitivity of the RAA assay was 2.23 copies per reaction, and no cross-reactions with any of the other 15 related respiratory bacterial pathogens were observed. Compared with the commercial real-time PCR assay used when testing 311 respiratory specimens, the RAA assay obtained 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity with a kappa value of 1.
Conclusions: These results demonstrate that the proposed RAA assay will be of benefit as a faster, sensitive, and specific alternative tool for the detection of M. pneumoniae.
Keywords: Detection; Molecular diagnostic technique; Mycoplasma pneumoniae; Recombinase; Recombinase-aided amplification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81401678/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81601778/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- FX-2019-05/Research Foundation of the Capital Institute of Pediatrics
- XTZD20180505/the Special Fund of the Pediatric Medical Coordinated Development Center of the Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

