Task shifting for point-of-care early infant diagnosis: a comparison of the quality of testing between nurses and laboratory personnel in Zimbabwe
- PMID: 31992332
- PMCID: PMC6986104
- DOI: 10.1186/s12960-020-0449-2
Task shifting for point-of-care early infant diagnosis: a comparison of the quality of testing between nurses and laboratory personnel in Zimbabwe
Abstract
Background: To decentralize point-of-care early infant diagnosis (POC EID), task shifting to cadres such as nurses is important. However, this should not compromise quality of testing through generating high rates of internal quality control (IQC) failures and long result turnaround times. We used data from a POC EID project in Zimbabwe to compare IQC rates and result return to caregivers for samples run on a POC EID technology (Alere q HIV 1/2 Detect) between nurses and laboratory-trained personnel to assess effects of task shifting on quality of testing.
Methods: This cross-sectional retrospective study used data from all 46 sites (10 hub and 36 spoke sites in Zimbabwe that piloted POC EID for routine clinical use from December 2016 to June 2017). IQC failure rates were downloaded from each POC EID platform and exported to excel to analyze IQC failure rates by type of operator. Turnaround time (TAT) from sample collection to issuing of results to caregiver was extracted from the EID test request form and uploaded into a project specific Excel-based database for analysis.
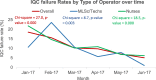
Results: A total of 1847 tests were conducted by 45 testers (12 laboratory-trained and 33 non-laboratory-trained personnel), including 165 errors. There were no significant differences in IQC failure rates between non-laboratory testers (137 [9.2%] of 14830 tests) and specialized laboratory-trained (28 [7.7%] of 364 tests; p = 0.354). Over time, IQC failure rates for both non-laboratory (χ2 = 18.5, p < 0.000) and specialized laboratory-trained testers (χ2 = 8.7, p < 0.003) decreased significantly. There were similar proportions of clients who were issued with results between samples processed by non-laboratory testers (1283 [98.9%] of 1297 tests) and samples processed by specialized laboratory-trained testers (315 [98.7%] of 319 tests; p = 0.790). The overall median turnaround time from sample collection to receipt of results by caregiver for samples run by laboratory-specialized testers was not statistically different from samples run by non-laboratory-specialized testers (1 day [IQR 0-3] versus 0 days [IQR 0-2]; p = 0.583).
Conclusions: Similar IQC failure rates and TATs between non-laboratory and specialized laboratory-trained operators suggest that non-specialized laboratory-trained personnel can perform POC EID equally well as specialized laboratory personnel.
Keywords: Early infant diagnosis; Internal quality controls; Point-of-care; Task shifting; Tester; Turnaaround time.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Global HIV & AIDS statistics — 2018 fact sheet [Internet]. UNAIDS; [cited 2019 May 30]. Available from: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet [Google Scholar]
-
- Violari Avy, Cotton Mark F., Gibb Diana M., Babiker Abdel G., Steyn Jan, Madhi Shabir A., Jean-Philippe Patrick, McIntyre James A. Early Antiretroviral Therapy and Mortality among HIV-Infected Infants. New England Journal of Medicine. 2008;359(21):2233–2244. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0800971. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bianchi F, Cohn J, Sacks E, Bailey B.R, Lemaire J, Machekano R. Evaluation of routine point-of-care intervention for early infant diagnosis of HIV: an observational study in eight African countries. Lancet, (364), 1236–1243 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources