A Novel Resistance Pathway for Calcineurin Inhibitors in the Human-Pathogenic Mucorales Mucor circinelloides
- PMID: 31992620
- PMCID: PMC6989107
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.02949-19
A Novel Resistance Pathway for Calcineurin Inhibitors in the Human-Pathogenic Mucorales Mucor circinelloides
Abstract
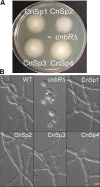
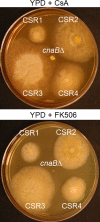
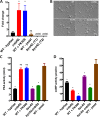
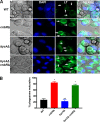
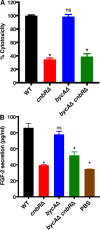
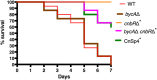
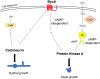
Mucormycosis is an emerging lethal fungal infection in immunocompromised patients. Mucor circinelloides is a causal agent of mucormycosis and serves as a model system to understand genetics in Mucorales. Calcineurin is a conserved virulence factor in many pathogenic fungi, and calcineurin inhibition or deletion of the calcineurin regulatory subunit (CnbR) in Mucor results in a shift from hyphal to yeast growth. We analyzed 36 calcineurin inhibitor-resistant or bypass mutants that exhibited hyphal growth in the presence of calcineurin inhibitors or in the yeast-locked cnbRΔ mutant background without carrying any mutations in known calcineurin components. We found that a majority of the mutants had altered sequence in a gene, named here bycA (
Keywords: Mucor; amino acid permease; calcineurin; dimorphism; drug resistance mechanisms; mucormycosis; protein kinase A.
Copyright © 2020 Vellanki et al.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

