Assessing connectivity despite high diversity in island populations of a malaria mosquito
- PMID: 31993086
- PMCID: PMC6976967
- DOI: 10.1111/eva.12878
Assessing connectivity despite high diversity in island populations of a malaria mosquito
Abstract
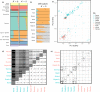
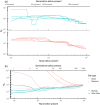
Documenting isolation is notoriously difficult for species with vast polymorphic populations. High proportions of shared variation impede estimation of connectivity, even despite leveraging information from many genetic markers. We overcome these impediments by combining classical analysis of neutral variation with assays of the structure of selected variation, demonstrated using populations of the principal African malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Accurate estimation of mosquito migration is crucial for efforts to combat malaria. Modeling and cage experiments suggest that mosquito gene drive systems will enable malaria eradication, but establishing safety and efficacy requires identification of isolated populations in which to conduct field testing. We assess Lake Victoria islands as candidate sites, finding one island 30 km offshore is as differentiated from mainland samples as populations from across the continent. Collectively, our results suggest sufficient contemporary isolation of these islands to warrant consideration as field-testing locations and illustrate shared adaptive variation as a useful proxy for connectivity in highly polymorphic species.
Keywords: Anopheles gambiae; gene drive technology; gene flow; malaria; migration.
© 2019 The Authors. Evolutionary Applications published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Aronesty, E. (2011). ea‐utils: Command‐line tools for processing biological sequencing data. [Computer software]. Retrieved from https://expressionanalysis.github.io/ea-utils
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

