The Inhibition of Inflammatory Signaling Pathway by Secretory Leukocyte Protease Inhibitor can Improve Spinal Cord Injury
- PMID: 31993863
- PMCID: PMC11448923
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-020-00799-1
The Inhibition of Inflammatory Signaling Pathway by Secretory Leukocyte Protease Inhibitor can Improve Spinal Cord Injury
Abstract
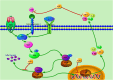
Spinal cord injury leads to loss of sensory motor functions below the damaged area, and can significantly affects physical and mental health. An effective spinal cord injury treatment is currently unavailable, in part, because of the intricacy of the brain, as well as the complex pathophysiological mechanism of the injury. Inflammation is an important biological process in multitudinous diseases, with no exception for spinal cord injury. Nuclear factor kappa beta (NF-κB) signaling pathway is a key inflammatory element, as it is involved in cell survival, apoptosis, proliferation, differentiation, and immune response. Activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway leads to the release of a large number of inflammatory factors that can affect tissue repair. Hence, the inhibition of inflammatory responses could improve the repair of injured spinal cord tissues. Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI) has anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial properties, and promotes wound healing. SLPI can bind to the promoter region of tumor necrosis factor-αand interleukin-8 (IL-8) to inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway. Additionally, SLPI can reduce secondary damages after spinal cord injury, and prevent further complications. In this report, we analyze the pathophysiological mechanism of spinal cord injury, the role of NF-κB signaling pathway following spinal cord injury, and how SLPI regulates the NF-κB signaling pathway to curtail inflammatory reaction.
Keywords: Ecretory leukocyte protease inhibitor; Inflammation; Nuclear factor kappa beta signaling pathway; Oxidative stress; Spinal cord injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Allison DJ, Ditor DS (2015) Immune dysfunction and chronic inflammation following spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 53:14–18 - PubMed
-
- Ambrosi N, Caro F, Guerrieri D et al (2018) SLPI expression on kidney biopsies correlates with better clinical outcomes. Transplantation 102:S326–S327
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

