The Function of NM23-H1/NME1 and Its Homologs in Major Processes Linked to Metastasis
- PMID: 31993913
- PMCID: PMC7109179
- DOI: 10.1007/s12253-020-00797-0
The Function of NM23-H1/NME1 and Its Homologs in Major Processes Linked to Metastasis
Abstract
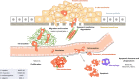
Metastasis suppressor genes (MSGs) inhibit different biological processes during metastatic progression without globally influencing development of the primary tumor. The first MSG, NM23 (non-metastatic clone 23, isoform H1) or now called NME1 (stands for non-metastatic) was identified some decades ago. Since then, ten human NM23 paralogs forming two groups have been discovered. Group I NM23 genes encode enzymes with evolutionarily highly conserved nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK) activity. In this review we summarize how results from NDPKs in model organisms converged on human NM23 studies. Next, we examine the role of NM23-H1 and its homologs within the metastatic cascade, e.g. cell migration and invasion, proliferation and apoptosis. NM23-H1 homologs are well known inhibitors of cell migration. Drosophila studies revealed that AWD, the fly counterpart of NM23-H1 is a negative regulator of cell motility by modulating endocytosis of chemotactic receptors on the surface of migrating cells in cooperation with Shibire/Dynamin; this mechanism has been recently confirmed by human studies. NM23-H1 inhibits proliferation of tumor cells by phosphorylating the MAPK scaffold, kinase suppressor of Ras (KSR), resulting in suppression of MAPK signalling. This mechanism was also observed with the C. elegans homolog, NDK-1, albeit with an inverse effect on MAPK activation. Both NM23-H1 and NDK-1 promote apoptotic cell death. In addition, NDK-1, NM23-H1 and their mouse counterpart NM23-M1 were shown to promote phagocytosis in an evolutionarily conserved manner. In summary, inhibition of cell migration and proliferation, alongside actions in apoptosis and phagocytosis are all mechanisms through which NM23-H1 acts against metastatic progression.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cell migration; Cftr; Dynamin; Metastasis inhibitor; NDPK; NM23; Phagocytosis; Phosphohistidine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The dosage-dependent effect exerted by the NM23-H1/H2 homolog NDK-1 on distal tip cell migration in C. elegans.Lab Invest. 2018 Feb;98(2):182-189. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2017.99. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Lab Invest. 2018. PMID: 28920944 Review.
-
The nucleoside diphosphate kinase NDK-1/NME1 promotes phagocytosis in concert with DYN-1/Dynamin.FASEB J. 2019 Oct;33(10):11606-11614. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900220R. Epub 2019 Jul 17. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31242766 Free PMC article.
-
The NM23-H1/H2 homolog NDK-1 is required for full activation of Ras signaling in C. elegans.Development. 2013 Aug;140(16):3486-95. doi: 10.1242/dev.094011. Development. 2013. PMID: 23900546 Free PMC article.
-
NDK-1, the homolog of NM23-H1/H2 regulates cell migration and apoptotic engulfment in C. elegans.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 21;9(3):e92687. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092687. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24658123 Free PMC article.
-
The metastasis suppressor Nm23 as a modulator of Ras/ERK signaling.J Mol Signal. 2014 May 12;9:4. doi: 10.1186/1750-2187-9-4. eCollection 2014. J Mol Signal. 2014. PMID: 24829611 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of Nm23-H1 to suppress breast cancer metastasis via redox regulation.Exp Mol Med. 2021 Mar;53(3):346-357. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00575-1. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Exp Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33753879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of action of NME metastasis suppressors - a family affair.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023 Dec;42(4):1155-1167. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10118-x. Epub 2023 Jun 24. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023. PMID: 37353690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metastasis suppressor genes in clinical practice: are they druggable?Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023 Dec;42(4):1169-1188. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10135-w. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023. PMID: 37749308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissecting the genetic complexity of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome via deep learning-powered genome analysis.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 11:2025.04.15.25325899. doi: 10.1101/2025.04.15.25325899. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40321247 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Kinase-catalyzed biotinylation for discovery and validation of substrates to multispecificity kinases NME1 and NME2.J Biol Chem. 2024 Aug;300(8):107588. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107588. Epub 2024 Jul 18. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39032654 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

