MicroRNA-based biomarkers for diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- PMID: 31994346
- PMCID: PMC7049510
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.13337
MicroRNA-based biomarkers for diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Abstract
Background: The development of biomarkers for the early detection of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is clinically important. We have developed miRNA biomarkers in sputum and plasma, respectively, for NSCLC. Herein, we evaluate whether integrated analysis of the miRNAs across the different types of specimens could improve the early detection of NSCLC.
Methods: Using reverse transcription PCR, we determined expressions of two miRNAs (miRs-31-5p and 210-3p) in sputum and three miRNAs (miRs-21-5p, 210-3p, and 486-5p) in plasma of a training cohort of 76 NSCLC patients and 72 cancer-free smokers. The results were validated in a testing cohort of 56 NSCLC patients and 55 cancer-free smokers.
Results: The panels of two sputum miRNAs and three plasma miRNAs had 65.8-75.0% sensitivities and 83.3-87.5% specificities for diagnosis of NSCLC in the training cohort. The individual sputum or plasma miRNA panel had a higher sensitivity for squamous cell carcinoma or adenocarcinoma of the lung, respectively. From the miRNAs, we optimized an integrated panel of biomarkers consisting of two sputum miRNAs (miRs-31-5p and 210-3p) and one plasma miRNA (miR-21-5p) that had higher sensitivity (85.5%) and specificity (91.7%) for diagnosis of NSCLC compared with the individual panels alone. Furthermore, the performance of the integrated panel of biomarkers was independent of histology and stage of NSCLC, and patients' age, sex, and ethnicity. The performance of the integrated panel of biomarkers was confirmed in the testing cohort.
Conclusions: Integrating biomarkers across different body fluids would synergistically improve the early detection of NSCLC.
Key points: Lung cancer is a heterogeneous disease and develops from complex aberrations. Integrating sputum and plasma miRNAs has higher accuracy than when they are used alone.
Keywords: Biomarkers; diagnosis; lung cancer; microRNA; plasma; sputum.
© 2020 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
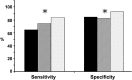
 Sputum biomarkers,
Sputum biomarkers,  plasma biomarkers,
plasma biomarkers,  integrated sputum and plasma biomarkers.
integrated sputum and plasma biomarkers.Similar articles
-
Integrating DNA methylation and microRNA biomarkers in sputum for lung cancer detection.Clin Epigenetics. 2016 Oct 19;8:109. doi: 10.1186/s13148-016-0275-5. eCollection 2016. Clin Epigenetics. 2016. PMID: 27777637 Free PMC article.
-
Early detection of lung adenocarcinoma in sputum by a panel of microRNA markers.Int J Cancer. 2010 Dec 15;127(12):2870-8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25289. Int J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21351266 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating miRNA panels as a novel non-invasive diagnostic, prognostic, and potential predictive biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Br J Cancer. 2024 Nov;131(8):1350-1362. doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02831-3. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39215192 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of differentially expressed circulating serum microRNA for the diagnosis and prognosis of Indian non-small cell lung cancer patients.Curr Probl Cancer. 2020 Aug;44(4):100540. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2020.100540. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Curr Probl Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32007320 Review.
-
microRNA and Lung Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;889:153-77. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-23730-5_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26659001 Review.
Cited by
-
MiRNAs in Lung Cancer: Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Potential.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Jul 1;12(7):1610. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12071610. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35885514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions and clinical significance of KLRG1 in the development of lung adenocarcinoma and immunotherapy.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jun 29;21(1):752. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08510-3. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34187403 Free PMC article.
-
Latest Research Progress of Liquid Biopsy in Tumor-A Narrative Review.Cancer Manag Res. 2024 Aug 16;16:1031-1042. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S479338. eCollection 2024. Cancer Manag Res. 2024. PMID: 39165347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-based therapies: A cog in the wheel of lung cancer defense.Mol Cancer. 2021 Mar 19;20(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01338-2. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33740988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of common microRNA between COPD and non-small cell lung cancer through pathway enrichment analysis.BMC Genom Data. 2021 Oct 12;22(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12863-021-00986-z. BMC Genom Data. 2021. PMID: 34635059 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL et al Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015; 65: 87‐108. - PubMed
-
- Belinsky SA, Liechty KC, Gentry FD et al Promoter hypermethylation of multiple genes in sputum precedes lung cancer incidence in a high‐risk cohort. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 3338–44. - PubMed
-
- Croce CM, Calin GA. miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell 2005; 122: 6–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

