Imported hepatopulmonary echinococcosis: first report of Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto (G1) in Bolivia
- PMID: 31994653
- PMCID: PMC7083390
- DOI: 10.1590/0037-8682-0046-2018
Imported hepatopulmonary echinococcosis: first report of Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto (G1) in Bolivia
Abstract
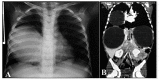
Hepatopulmonary hydatidosis in young children is a rare and atypical presentation of Echinococcus granulosus infection. We report the first case of cystic echinococcosis caused by a microvariant of E. granulosus sensu stricto. Chemotherapy and systemic corticoids were administered before curative surgery was performed. Recurrence was not observed for more than 24 months of follow-up.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Minimal access surgery for multiorgan hydatid cysts.Afr J Paediatr Surg. 2010 Jan-Apr;7(1):40-2. doi: 10.4103/0189-6725.59362. Afr J Paediatr Surg. 2010. PMID: 20098012
-
[Echinococcus granulosus (cystic echinococcosis)].Praxis (Bern 1994). 2003 Dec 17;92(51-52):2185-8; quiz 2189, 2227. doi: 10.1024/0369-8394.92.51.2185. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2003. PMID: 14727474 Review. German. No abstract available.
-
A novel zoonotic genotype related to Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto from southern Ethiopia.Int J Parasitol. 2016 Sep;46(10):663-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 May 12. Int J Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 27181929
-
Molecular identification of cystic echinococcosis in humans and pigs reveals the presence of both Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto and Echinococcus canadensis G6/G7 in the hyperendemic focus of the Republic of Moldova.Parasitol Res. 2019 Oct;118(10):2857-2861. doi: 10.1007/s00436-019-06432-5. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Parasitol Res. 2019. PMID: 31435765
-
Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato genotypes infecting humans--review of current knowledge.Int J Parasitol. 2014 Jan;44(1):9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2013.08.008. Epub 2013 Nov 19. Int J Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 24269720 Review.
Cited by
-
Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto, Echinococcus ortleppi; and E. intermedius (G7) are present in Bolivia.Parasitology. 2020 Aug;147(9):949-956. doi: 10.1017/S0031182020000529. Epub 2020 Apr 1. Parasitology. 2020. PMID: 32234095 Free PMC article.
-
Past and present of cystic echinococcosis in Bolivia.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Jun 17;15(6):e0009426. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009426. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34138855 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kinkar L, Laurimäe T, Acosta-Jamett G, Andresiuk V, Balkaya I, Casulli A, et al. Global phylogeography and genetic diversity of the zoonotic tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto genotype G1. Int J Parasitol. 2018;48(9-10):729–742. - PubMed
-
- Bowles J, Blair D, McManus DP. Genetic variants within the genus Echinococcus identified by mitochondrial DNA sequencing. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992;54(2):165–173. - PubMed
-
- Rodero Franganillo A, Delgado JV, Rodero Serrano E. Primitive andalusian livestock and their implications in the discovery of America. Archivos de Zootecnia. 1992;41(154):383–400.
-
- Larrieu EJ, Frider B. Human cystic echinococcosis: contributions to the natural history of the disease. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 2001;95(7):679–687. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

