Canadian Burden of Skin Disease From 1990 to 2017: Results From the Global Burden of Disease 2017 Study
- PMID: 31994902
- PMCID: PMC7109598
- DOI: 10.1177/1203475420902047
Canadian Burden of Skin Disease From 1990 to 2017: Results From the Global Burden of Disease 2017 Study
Abstract
Background: Skin diseases can have high morbidity that can be costly to society and individuals. To date, there has been no comprehensive assessment of the burden of skin disease in Canada.
Objectives: To evaluate the burden of 18 skin and subcutaneous diseases from 1990 to 2017 in Canada using the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) data.
Methods: The 2017 GBD study measures health loss from 359 diseases and injuries in 195 countries; we evaluated trends in population health in Canada from 1990 to 2017 using incidence, prevalence, mortality, years of life lost (YLLs), years lived with disability (YLDs), and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). Data are presented as rates (per 100 000), counts, or percent change with the uncertainty interval in brackets.
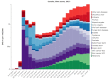
Results: From 1990 to 2017 for all skin diseases, DALY rates increased by 8% to 971 per 100 000 (674-1319), YLD rates increased by 8% to 897 per 100 000 (616-1235), YLL rates increased by 4% to 74 per 100 000 (53-89), and death rates increased by 18% to 5 per 100 000 (3-6). DALY rates for melanoma increased by 2% to 54 per 100 000 (39-68), for keratinocyte carcinoma by 14% to 17 per 100 000 (16-19), and for skin and subcutaneous disease by 8% to 900 per 100 000 (619-1233). The observed over expected ratios were higher for skin and subcutaneous disease (1.37) and keratinocyte carcinoma (1.17) and were lower for melanoma (0.73).
Conclusions: The burden of skin disease has increased in Canada since 1990. These results can be used to guide health policy regarding skin disease in Canada.
Keywords: disability; incidence; prevalence; skin disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical