Fetal and Maternal Responses to Dexmedetomidine Intrathecal Application During Cesarean Section: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 31995551
- PMCID: PMC7001518
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.918523
Fetal and Maternal Responses to Dexmedetomidine Intrathecal Application During Cesarean Section: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
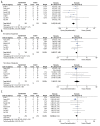
BACKGROUND Intrathecal dexmedetomidine (DEX) can improve the blockade of spinal anesthesia, but there is no clear conclusion on whether it has an effect on the fetus during cesarean section. Our meta-analysis evaluated the safety and efficacy of intrathecal DEX in cesarean delivery. MATERIAL AND METHODS We searched Cochrane, Embase, PubMed, and CBM for eligible studies, and used the Revised Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool (RoB 2.0) to assess the risk of bias of each study. RevMan was used for statistical analyses. We have registered this meta-analysis on PROSPERO (CRD42019120995). RESULTS The meta-analysis included 10 RCTs, but only 5 were prospectively registered. The results of preregistration studies, including the 1- or 5-min Apgar score (mean difference [MD], -0.03; 95% confidence intervals [CI], -0.16 to 0.10; P=0.64 or MD, 0.00; 95% CI, -0.09 to 0.09; P=1), the umbilical arterial oxygen or carbon dioxide partial pressure (MD, 0.90; 95% CI, -4.92 to 6.72; P=0.76 or MD, 1.20; 95% CI, -2.06 to 4.46; P=0.47), and the cord blood pH (MD, -0.01; 95% CI, -0.05 to 0.03; P=0.72), showed that intrathecal DEX had no significant difference in neonatal outcomes compared with placebo. In maternal outcomes, intrathecal DEX significantly prolonged postoperative pain-free period and reduced the incidence of postoperative shivering, which did not increase spinal anesthesia-associated adverse effects. CONCLUSIONS Intrathecal DEX is safe for the fetus during cesarean section and can improve the blockade effects of spinal anesthesia on puerperae.
Figures
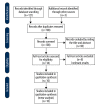

 low risk;
low risk;
 some concerns;
some concerns;
 high risk.
high risk.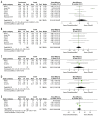



Similar articles
-
Effect of intrathecal dexmedetomidine on preventing shivering in cesarean section after spinal anesthesia: a meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Nov 2;12:3775-3783. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S178665. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 30464408 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of intrathecal dexmedetomidine on cesarean section during spinal anesthesia: a meta-analysis of randomized trials.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Aug 21;13:2933-2939. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S207812. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31686777 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant for single spinal anesthesia in patients undergoing cesarean section: a system review and meta-analysis.J Int Med Res. 2020 May;48(5):300060520913423. doi: 10.1177/0300060520913423. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32466699 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and safety of intravenous application of dexmedetomidine for cesarean section under general anesthesia: a meta-analysis of randomized trials.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Mar 25;13:965-974. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S197165. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 30988599 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of 5-μg Dose of Dexmedetomidine in Combination With Intrathecal Bupivacaine on Spinal Anesthesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Ther. 2020 Apr;42(4):676-690.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2020.02.009. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Clin Ther. 2020. PMID: 32222361
Cited by
-
Effect of Epidural Dexmedetomidine as an Adjuvant to Local Anesthetics for Labor Analgesia: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Oct 27;2021:4886970. doi: 10.1155/2021/4886970. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34745286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sufentanil vs. Dexmedetomidine as Neuraxial Adjuvants in Cesarean Section: A Mono-Centric Retrospective Comparative Study.J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 21;11(22):6868. doi: 10.3390/jcm11226868. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36431344 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuncts for neuraxial anaesthesia in obstetrics.BJA Educ. 2025 Jun;25(6):219-225. doi: 10.1016/j.bjae.2025.01.006. Epub 2025 May 15. BJA Educ. 2025. PMID: 40496203 Review. No abstract available.
-
Intrathecal dexmedetomidine improves epidural labor analgesia effects: a randomized controlled trial.J Int Med Res. 2021 Apr;49(4):300060521999534. doi: 10.1177/0300060521999534. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33827306 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Karlström A. Women’s self-reported experience of unplanned caesarean section: Results of a Swedish study. Midwifery. 2017;50:253–58. - PubMed
-
- Practice Guidelines for Obstetric Anesthesia. An updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Obstetric Anesthesia and the Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology. Anesthesiology. 2016;124:270–300. - PubMed
-
- Campbell JP, Stocks GM. Management of hypotension with vasopressors at caesarean section under spinal anaesthesia-have we found the Holy Grail of obstetric anaesthesia? Anaesthesia. 2018;73:3–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

