A Randomized Trial of Distal Diuretics versus Dietary Sodium Restriction for Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 31996411
- PMCID: PMC7062227
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2019090905
A Randomized Trial of Distal Diuretics versus Dietary Sodium Restriction for Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
Background: Distal diuretics are considered less effective than loop diuretics in CKD. However, data to support this perception are limited.
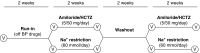
Methods: To investigate whether distal diuretics are noninferior to dietary sodium restriction in reducing BP in patients with CKD stage G3 or G4 and hypertension, we conducted a 6-week, randomized, open-label crossover trial comparing amiloride/hydrochlorothiazide (5 mg/50 mg daily) with dietary sodium restriction (60 mmol per day). Antihypertension medication was discontinued for a 2-week period before randomization. We analyzed effects on BP, kidney function, and fluid balance and related this to renal clearance of diuretics.
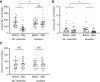
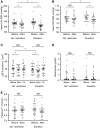
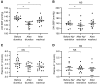
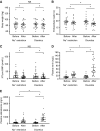
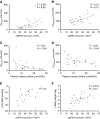
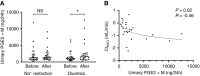
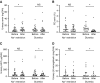
Results: A total of 26 patients (with a mean eGFR of 39 ml/min per 1.73 m2) completed both treatments. Dietary sodium restriction reduced sodium excretion from 160 to 64 mmol per day. Diuretics produced a greater reduction in 24-hour systolic BP (SBP; from 138 to 124 mm Hg) compared with sodium restriction (from 134 to 129 mm Hg), as well as a significantly greater effect on extracellular water, eGFR, plasma renin, and aldosterone. Both interventions resulted in a similar decrease in body weight and NT-proBNP. Neither approaches decreased albuminuria significantly, whereas diuretics did significantly reduce urinary angiotensinogen and β2-microglobulin excretion. Although lower eGFR and higher plasma indoxyl sulfate correlated with lower diuretic clearance, the diuretic effects on body weight and BP at lower eGFR were maintained. During diuretic treatment, higher PGE2 excretion correlated with lower free water clearance, and four patients developed mild hyponatremia.
Conclusions: Distal diuretics are noninferior to dietary sodium restriction in reducing BP and extracellular volume in CKD. Diuretic sensitivity in CKD is maintained despite lower diuretic clearance.
Clinical trial registry name and registration number: DD-study: Diet or Diuretics for Salt-sensitivity in Chronic Kidney Disease (DD), NCT02875886.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; clinical hypertension; clinical trial; diuretics; pharmacokinetics; water-electrolyte balance.
Copyright © 2020 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of Dietary Sodium Restriction in Kidney Transplant Recipients Treated With Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockade: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Am J Kidney Dis. 2016 Jun;67(6):936-44. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.11.026. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016. PMID: 26803690 Clinical Trial.
-
A Self-management Approach for Dietary Sodium Restriction in Patients With CKD: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Am J Kidney Dis. 2020 Jun;75(6):847-856. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.10.012. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020. PMID: 31955921 Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized trial of sodium-restriction on kidney function, fluid volume and adipokines in CKD patients.BMC Nephrol. 2014 Apr 4;15:57. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-15-57. BMC Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24708818 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;956:307-325. doi: 10.1007/5584_2016_84. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 27873228 Review.
-
Vitamin D receptor activator and dietary sodium restriction to reduce residual urinary albumin excretion in chronic kidney disease (ViRTUE study): rationale and study protocol.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016 Jul;31(7):1081-7. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfv033. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016. PMID: 25744274 Review.
Cited by
-
Diuretics in patients with chronic kidney disease.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2025 Apr;21(4):264-278. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00918-x. Epub 2025 Jan 7. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39775051 Review.
-
Efficacy of tolvaptan in postoperative volume therapy for acute Stanford type A aortic dissection.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Feb 21;23(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03125-x. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 36803437 Free PMC article.
-
Thiazide diuretics are back in CKD: the case of chlorthalidone.Clin Kidney J. 2022 Sep 7;16(1):41-51. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfac198. eCollection 2023 Jan. Clin Kidney J. 2022. PMID: 36726437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What is central to renal nutrition: protein or sodium intake?Clin Kidney J. 2023 Jun 29;16(11):1824-1833. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfad151. eCollection 2023 Nov. Clin Kidney J. 2023. PMID: 37915942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estimated 24-h urinary sodium excretion and risk of end-stage kidney disease.iScience. 2023 Apr 23;26(5):106728. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106728. eCollection 2023 May 19. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37216108 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Faucon AL, Flamant M, Metzger M, Boffa JJ, Haymann JP, Houillier P, et al. .; NephroTest Study Group: Extracellular fluid volume is associated with incident end-stage kidney disease and mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 96: 1020–1029, 2019. - PubMed
-
- Hung SC, Kuo KL, Peng CH, Wu CH, Lien YC, Wang YC, et al. .: Volume overload correlates with cardiovascular risk factors in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 85: 703–709, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Vidal-Petiot E, Metzger M, Faucon AL, Boffa JJ, Haymann JP, Thervet E, et al. .; NephroTest Study Group: Extracellular fluid volume is an independent determinant of uncontrolled and resistant hypertension in chronic kidney disease: A nephroTest cohort study. J Am Heart Assoc 7: e010278, 2018. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Essig M, Escoubet B, de Zuttere D, Blanchet F, Arnoult F, Dupuis E, et al. .: Cardiovascular remodelling and extracellular fluid excess in early stages of chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23: 239–248, 2008. - PubMed
-
- McMahon EJ, Campbell KL, Bauer JD, Mudge DW: Altered dietary salt intake for people with chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2: CD010070, 2015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

