RACK1 promotes cancer progression by increasing the M2/M1 macrophage ratio via the NF-κB pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 31997535
- PMCID: PMC7138402
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12644
RACK1 promotes cancer progression by increasing the M2/M1 macrophage ratio via the NF-κB pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
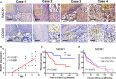
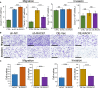
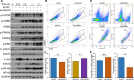
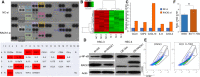
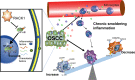
Receptor for activated C kinase 1 (RACK1) has been shown to promote oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) progression, and RACK1 expression levels have been negatively correlated with prognosis in patients with OSCC. Here, we investigated the impact of RACK1 OSCC expression on the recruitment and differentiation of tumor-associated macrophages. High RACK1 expression in OSCC cells correlated with increased M2 macrophage infiltration in tumor samples from a clinical cohort study. Moreover, the combination of RACK1 expression and the M2/M1 ratio could successfully predict prognosis in OSCC. OSCC cells with high RACK1 expression inhibited the migration of THP-1 cells, promoted M2-like macrophage polarization in vitro, and increased the proportion of M2-like macrophages in a xenograft mouse model. Moreover, both M1- and M2-like macrophage polarization-associated proteins were induced in macrophages cocultured with RACK1-silenced cell supernatant. A mechanistic study revealed that the expression and secretion of C-C motif chemokine 2 (CCL2), C-C motif chemokine 5 (CCL5), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-1 (IL-1) are closely related to RACK1 expression. In addition, blocking nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) could promote M2-like macrophage polarization. These results indicate that RACK1 and the M2/M1 ratio are predictors of a poor prognosis in OSCC. RACK1 promotes M2-like polarization by regulating NF-κB and could be used as a potential therapeutic target for antitumor immunity.
Keywords: NF-κB; RACK1; macrophage polarization; oral squamous cell carcinoma; tumor-associated macrophages.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by FEBS Press and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alves AM, Diel LF and Lamers ML (2018) Macrophages and prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review. J Oral Pathol Med 47, 460–467. - PubMed
-
- Balermpas P, Rodel F, Liberz R, Oppermann J, Wagenblast J, Ghanaati S, Harter PN, Mittelbronn M, Weiss C, Rodel C et al (2014) Head and neck cancer relapse after chemoradiotherapy correlates with CD163+ macrophages in primary tumour and CD11b+ myeloid cells in recurrences. Br J Cancer 111, 1509–1518. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F, Charles KA and Mantovani A (2005) Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and promotion of malignant disease. Cancer Cell 7, 211–217. - PubMed
-
- Berns H, Humar R, Hengerer B, Kiefer FN and Battegay EJ (2000) RACK1 is up‐regulated in angiogenesis and human carcinomas. FASEB J 14, 2549–2558. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

