Seroprevalence of human brucellosis and molecular characteristics of Brucella strains in Inner Mongolia Autonomous region of China, from 2012 to 2016
- PMID: 31997725
- PMCID: PMC7034055
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1720528
Seroprevalence of human brucellosis and molecular characteristics of Brucella strains in Inner Mongolia Autonomous region of China, from 2012 to 2016
Abstract
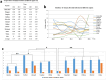
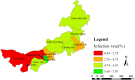
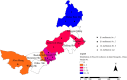
In the present study, a total of 1102304 serum samples were collected to detected human brucellosis between the years 2012 and 2016 in Inner Mongolia. Overall, an average of 3.79% anti-Brucella positive in Inner Mongolia was presented but the range of positive rates were among 0.90 to 7.07% in 12 regions. Seroprevalence of human brucellosis increased gradually from 2012 to 2016. However, the incidence rate of human brucellosis showed a declining trend. One hundred and seven Brucella strains were isolated and identified as B. melitensis species, and B. melitensis biovar 3 was the predominant biovar. MLVA-11 genotypes 116 was predominant and had crucial epidemiology to the human population. All 107 strains tested were sorted into 75 MLVA-16 genotypes, with 54 single genotypes representing unique isolates. This result revealed that these Brucellosis cases had epidemiologically unrelated and sporadic characteristics. The remaining 21 shared genotypes among two to four strains, confirming the occurrence of cross-infection and multiple outbreaks. Extensive genotype-events were observed between strains from this study and Kazakhstan, Mongolia, and Turkey, these countries were key members of the grassland silk road. Long-time trade in small ruminants (sheep) in these countries has possibly promoted the spread of Brucella spp. in these regions.
Keywords: Brucella melitensis; Inner Mongolia; MLVA; Serology; molecular epidemiology.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Epidemiologically characteristics of human brucellosis and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of Brucella melitensis in Hinggan League of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China.Infect Dis Poverty. 2020 Jun 29;9(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s40249-020-00697-0. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020. PMID: 32600403 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence trend of human brucellosis and MLVA genotyping characteristics of Brucella melitensis in Shaanxi Province, China, during 2008-2020.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2022 Jul;69(4):e423-e434. doi: 10.1111/tbed.14320. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2022. PMID: 34510783
-
Molecular epidemiology of Brucella abortus strains from cattle in Inner Mongolia, China.Prev Vet Med. 2020 Oct;183:105080. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2020.105080. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Prev Vet Med. 2020. PMID: 32919319
-
Incidence and control of brucellosis in the Near East region.Vet Microbiol. 2002 Dec 20;90(1-4):81-110. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(02)00248-1. Vet Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12414137 Review.
-
From the discovery of the Malta fever's agent to the discovery of a marine mammal reservoir, brucellosis has continuously been a re-emerging zoonosis.Vet Res. 2005 May-Jun;36(3):313-26. doi: 10.1051/vetres:2005003. Vet Res. 2005. PMID: 15845228 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular investigation of infection sources and transmission chains of brucellosis in Zhejiang, China.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020 Dec;9(1):889-899. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1754137. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020. PMID: 32284015 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity atlas of Brucella melitensis strains from Sichuan Province, China.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Jan 14;25(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03739-x. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39810148 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Epidemiological Study of a Human Brucellosis Outbreak - Weihai City, Shandong Province, China, 2022.China CDC Wkly. 2024 Mar 22;6(12):230-234. doi: 10.46234/ccdcw2024.046. China CDC Wkly. 2024. PMID: 38633432 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the Seroprevalence of Brucella Antibodies and Characterization of Field Strains in Immunized Dairy Cows by B. abortus A19.Vet Sci. 2024 Jun 28;11(7):288. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11070288. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39057972 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiologically characteristics of human brucellosis and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of Brucella melitensis in Hinggan League of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China.Infect Dis Poverty. 2020 Jun 29;9(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s40249-020-00697-0. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020. PMID: 32600403 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
