The influence of variations of furanosesquiterpenoids content of commercial samples of myrrh on their biological properties
- PMID: 31997905
- PMCID: PMC6978635
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2019.07.007
The influence of variations of furanosesquiterpenoids content of commercial samples of myrrh on their biological properties
Abstract
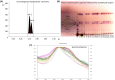
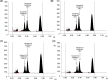
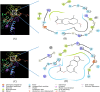
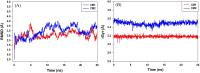
Myrrh is an oleo-gum-resin produced in the stem of Commiphora myrrha (Burseraceae) and used for centuries for different medicinal purposes. The present work was designed to evaluate the cytotoxic and antioxidant properties of seventeen myrrh samples (S1-S17) obtained from different retail markets of Saudi Arabia and Yemen regions, along with two furanosesquiterpenoids (CM-1 and CM-2). The cytotoxicity assay was carried out on HepG2, MCF-7 and HUVEC cell lines. S2, S5, S10, S12, CM-1, CM-2 exhibited significant cytotoxicity against HepG2/MCF-7 cell lines [IC50 (μg/mL): 13.8/10, 14/10, 14.5/11.3, 18/13.2, 9.5/12.5, 10/15.8, respectively) compare to vinblastin (IC50 (μg/mL): 2/2.5) whereas the remaining samples were found as mild active or inactive. The antioxidant properties of the samples were tested by β-carotene-bleaching and DPPH free radical scavenging methods where the samples S8 (1000 μg/mL) exhibited the highest β-carotene bleaching (76.2%) and free radical scavenging activity (79.8%). The HPTLC analysis was performed on NP-HPTLC plate using toluene, chloroform and glacial acetic acid as mobile phase in ratio of 7:2.9:0.1 (V/V/V). The validated HPTLC method furnished sharp, intense and compact peaks of CM-1 and CM-2 at Rf = 0.39 and 0.44, respectively. The highest/lowest content of CM-1 and CM-2 were found in S12/S5 and S5/S17, respectively. The molecular docking studies of CM-1 and CM-2 with human DNA topoisomerase IIα have shown that both the compounds were bound the active sites of the respective enzymes. Molecular dynamics simulation studies further confirmed that the interactions of CM-1 and CM-2 with topoisomerase were stable in nature. This study will help us in selection of appropriate myrrh sample for the greater benefits of the population in the Middle East region.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Cytotoxicity; Furanosesquiterpenoids; HPTLC; Molecular docking; Myrrh.
© 2019 Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of King Saud University.
Figures
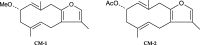
References
-
- AI-Harbi M., Qureshi S., Ahmed M., Rafatullah S., Shah A. Effect of Commiphora molmol (oleo-gum-resin) on the cytological and biochemical changes induced by cyclophosphamide in mice. Am. J. Chin. Med. 1994;22:77–82. - PubMed
-
- AlAjmi M.F., Alam P., Rehman M.T., Husain M.F., Khan A.A., Siddiqui N.A., Hussain A., Kalam M.A., Parvez M.K. Interspecies anticancer and antimicrobial activities of genus Solanum and estimation of rutin by validated UPLC-PDA method. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018;6040815:1–13. - PMC - PubMed
-
- AlAjmi M.F., Rehman M.T., Hussain A., Rather G.M. Pharmacoinformatics approach for the identification of Polo-like kinase-1 inhibitors from natural sources as anti-cancer agents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018;116:173–181. - PubMed
-
- Al-Harbi M., Qureshi S., Raza M., Ahmed M., Afzal M., Shah A.H. Gastric antiulcer and cytoprotective effect of Commiphora molmol in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1997;55:141–150. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

