Evaluation of serum lipid, lipoprotein, and apolipoprotein levels in psoriatic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies
- PMID: 31997997
- PMCID: PMC6986295
- DOI: 10.5114/ada.2019.91420
Evaluation of serum lipid, lipoprotein, and apolipoprotein levels in psoriatic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies
Abstract
Introduction: Psoriasis is a T cell-mediated inflammatory skin disease in which fatty acids may be a link between psoriasis and its comorbidity.
Aim: The present meta-analysis aimed to evaluate lipid, lipoprotein, and apolipoprotein levels in the psoriatic patients compared with the control subjects.
Material and methods: Four databases, including Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, and Cochrane Library were searched until July 2017. All records analysed were case-control studies. The quality of the questionnaires was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS). A random-effects meta-analysis was done by Rev Man 5.3 using mean difference (MD) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
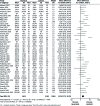
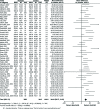
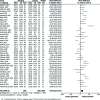
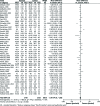
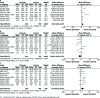
Results: Out of 580 studies identified in four databases, 49 studies were included and analysed in this meta-analysis. The results showed that MD of total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL, VLDL, HDL, Lp(a), Apo A1, and Apo B levels in the patients compared with the controls were (MD = 13.74 mg/dl; 95% CI: 7.72-19.75; p< 0.00001), (MD = 26.04 mg/dl; 95% CI: 20.77-31.31; p< 0.00001), (MD = 11.41 mg/dl; 95% CI: 6.26-16.57; p< 0.0001), (MD = 4.82 mg/dl; 95% CI: 3.63-6.00; p< 0.00001), (MD = -2.78 mg/dl; 95% CI: -4.53 - -1.03; p< 0.002), (MD = 8.51 mg/dl; 95% CI: 4.86-12.17; p< 0.0001), (MD = -6.60 mg/dl; 95% CI: -13.96 - 0.75; p< 0.08), and (MD = 9.70 mg/dl; 95% CI: 3.02-16.39; p< 0.004), respectively.
Conclusions: This meta-analysis identified abnormality of serum lipid, lipoprotein, and apolipoproteinprofiles in psoriatic patients compared with the controls as well as possibly a greater risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular (CV) accidents in the patients.
Keywords: apolipoprotein; lipid; lipoprotein; psoriasis; serum.
Copyright © 2019 Termedia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Irimie M, Oanţă A, Irimie CA, et al. Cardiovascular risk factors in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis: a case-control study on the Brasov County population. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat 2015; 23: 28-35. - PubMed
-
- Romaní J, Caixàs A, Carrascosa JM, et al. Effect of narrowband ultraviolet B therapy on inflammatory markers and body fat composition in moderate to severe psoriasis.Br J Dermatol 2012; 166: 1237-44. - PubMed
-
- Nemati H, Khodarahmi R, Sadeghi M, et al. Antioxidant status in patients with psoriasis. Cell Biochem Funct 2014; 32: 268-73. - PubMed
-
- Puig-Sanz L. Psoriasis, a systemic disease? Actas Dermosifiliogr 2007; 98: 396-402. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
