Muscarinic Modulation of Morphologically Identified Glycinergic Neurons in the Mouse PreBötzinger Complex
- PMID: 31998077
- PMCID: PMC6962194
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00562
Muscarinic Modulation of Morphologically Identified Glycinergic Neurons in the Mouse PreBötzinger Complex
Abstract
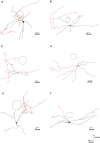
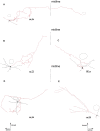
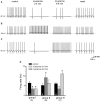
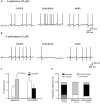
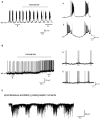
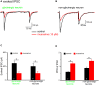
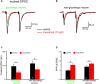
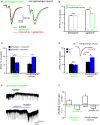
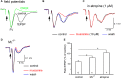
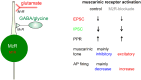
The cholinergic system plays an essential role in central respiratory control, but the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. We used whole-cell recordings in brainstem slices from juvenile mice expressing enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) under the control of the glycine transporter type 2 (GlyT2) promoter, to examine muscarinic modulation of morphologically identified glycinergic neurons in the preBötzinger complex (preBötC), an area critical for central inspiratory rhythm generation. Biocytin-filled reconstruction of glycinergic neurons revealed that the majority of them had few primary dendrites and had axons arborized within their own dendritic field. Few glycinergic neurons had axon collaterals extended towards the premotor/motor areas or ran towards the contralateral preBötC, and had more primary dendrites and more compact dendritic trees. Spontaneously active glycinergic neurons fired regular spikes, or less frequently in a "burst-like" pattern at physiological potassium concentration. Muscarine suppressed firing in the majority of regular spiking neurons via M2 receptor activation while enhancing the remaining neurons through M1 receptors. Interestingly, rhythmic bursting was augmented by muscarine in a small group of glycinergic neurons. In contrast to its heterogeneous modulation of glycinergic neuronal excitability, muscarine generally depressed inhibitory and excitatory synaptic inputs onto both glycinergic and non-glycinergic preBötC neurons, with a stronger effect on inhibitory input. Notably, presynaptic muscarinic attenuation of excitatory synaptic input was dependent on M1 receptors in glycinergic neurons and on M2 receptors in non-glycinergic neurons. Additional field potential recordings of excitatory synaptic potentials in the M2 receptor knockout mice indicate that glycinergic and non-glycinergic neurons contribute equally to the general suppression by muscarine of excitatory activity in preBötC circuits. In conclusion, our data show that preBötC glycinergic neurons are morphologically heterogeneous, and differ in the properties of synaptic transmission and muscarinic modulation in comparison to non-glycinergic neurons. The dominant and cell-type-specific muscarinic inhibition of synaptic neurotransmission and spiking may contribute to central respiratory disturbances in high cholinergic states.
Keywords: glycine; inhibitory neurotransmission; morphometric analysis; muscarinic acetylcholine receptors; preBötzinger complex.
Copyright © 2020 Zheng, Nixdorf-Bergweiler, Edelmann, van Brederode and Alzheimer.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

