Vitamin D Binding Protein: A Historic Overview
- PMID: 31998239
- PMCID: PMC6965021
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00910
Vitamin D Binding Protein: A Historic Overview
Abstract
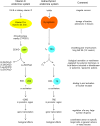
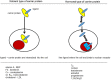
Vitamin D and all its metabolites are bound to a specific vitamin D binding protein, DBP. This protein was originally first discovered by its worldwide polymorphism and called Group-specific Component (GC). We now know that DBP and GC are the same protein and appeared early in the evolution of vertebrates. DBP is genetically the oldest member of the albuminoid family (including albumin, α-fetoprotein and afamin, all involved in transport of fatty acids or hormones). DBP has a single binding site for all vitamin D metabolites and has a high affinity for 25OHD and 1,25(OH)2D, thereby creating a large pool of circulating 25OHD, which prevents rapid vitamin D deficiency. DBP of higher vertebrates (not amphibians or reptiles) binds with very high affinity actin, thereby preventing the formation of polymeric actin fibrils in the circulation after tissue damage. Megalin is a cargo receptor and is together with cubilin needed to reabsorb DBP or the DBP-25OHD complex, thereby preventing the urinary loss of these proteins and 25OHD. The total concentrations of 25OHD and 1,25(OH)2D in DBP null mice or humans are extremely low but calcium and bone homeostasis remain normal. This is the strongest argument for claiming that the "free hormone hypothesis" also applies to the vitamin D hormone, 1,25(OH)2D. DBP also transports fatty acids, and can play a role in the immune system. DBP is genetically very polymorphic with three frequent alleles (DBP/GC 1f, 1s, and 2) but in total more than 120 different variants but its health consequences, if any, are not understood. A standardization of DBP assays is essential to further explore the role of DBP in physiology and diseases.
Keywords: 1,25-dihydoxyvitamin D; 25-hydoxyvitamin D; actin; megalin; vitamin D; vitamin D binding protein (DBP).
Copyright © 2020 Bouillon, Schuit, Antonio and Rastinejad.
Figures




References
-
- Thomas WC, Morgan HG, Connor TB, Haddock L, Bills CE, Howard JE. Studies of antiricketic activity in sera from patients with disorders of calcium metabolism and preliminary observations on the mode of transport of vitamin D in human serum. J Clin Invest. (1959) 38:1078–85. 10.1172/JCI103884 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

