Immunological Outcomes Mediated Upon Binding of Heat Shock Proteins to Scavenger Receptors SCARF1 and LOX-1, and Endocytosis by Mononuclear Phagocytes
- PMID: 31998315
- PMCID: PMC6968791
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03035
Immunological Outcomes Mediated Upon Binding of Heat Shock Proteins to Scavenger Receptors SCARF1 and LOX-1, and Endocytosis by Mononuclear Phagocytes
Abstract
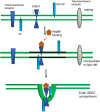
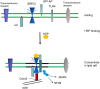
Heat shock proteins (HSP) are a highly abundant class of molecular chaperones that can be released into the extracellular milieu and influence the immune response. HSP release can occur when cells undergo necrosis and exude their contents. However, HSPs are also secreted from intact cells, either in free form or in lipid vesicles including exosomes to react with receptors on adjacent cells. Target cells are able recognize extracellular HSPs through cell surface receptors. These include scavenger receptors (SR) such as class E member oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1, aka OLR1, Clec8A, and SR-E1) and scavenger receptor class F member 1 (SCARF1, aka SREC1). Both receptors are expressed by dendritic cells (DC) and macrophages. These receptors can bind HSPs coupled to client binding proteins and deliver the chaperone substrate to the pathways of antigen processing in cells. SR are able to facilitate the delivery of client proteins to the proteasome, leading to antigen processing and presentation, and stimulation of adaptive immunity. HSPs may also may be involved in innate immunity through activation of inflammatory signaling pathways in a mechanism dependent on SR and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) on DC and macrophages. We will discuss the pathways by which HSPs can facilitate uptake of protein antigens and the receptors that regulate the ensuing immune response.
Keywords: dendritic; heat shock proteins; immunity; macrophage; scavenger receptor.
Copyright © 2020 Murshid, Borges, Bonorino, Lang and Calderwood.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emerging roles for scavenger receptor SREC-I in immunity.Cytokine. 2015 Oct;75(2):256-60. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.02.009. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 25767073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hsp110 and Grp170, members of the Hsp70 superfamily, bind to scavenger receptor-A and scavenger receptor expressed by endothelial cells-I.Eur J Immunol. 2007 Aug;37(8):2268-79. doi: 10.1002/eji.200737127. Eur J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17615582
-
Scavenger receptors and heat-shock protein-mediated antigen cross-presentation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Aug;32(Pt 4):633-5. doi: 10.1042/BST0320633. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 15270694
-
Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 delivers heat shock protein 60-fused antigen into the MHC class I presentation pathway.J Immunol. 2010 Aug 15;185(4):2306-13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903214. Epub 2010 Jul 14. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20631313
-
SCARF1: a multifaceted, yet largely understudied, scavenger receptor.Inflamm Res. 2018 Aug;67(8):627-632. doi: 10.1007/s00011-018-1154-7. Epub 2018 May 3. Inflamm Res. 2018. PMID: 29725698 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Atherosclerosis and Inflammation: Insights from the Theory of General Pathological Processes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 26;24(9):7910. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097910. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triple knockdown of CDC37, HSP90-alpha and HSP90-beta diminishes extracellular vesicles-driven malignancy events and macrophage M2 polarization in oral cancer.J Extracell Vesicles. 2020 May 31;9(1):1769373. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2020.1769373. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020. PMID: 33144925 Free PMC article.
-
Heat Shock Proteins, a Double-Edged Sword: Significance in Cancer Progression, Chemotherapy Resistance and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 14;16(8):1500. doi: 10.3390/cancers16081500. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of SREC-Ⅰ in Innate Immunity to Aspergillus fumigatus Keratitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Jul 1;62(9):12. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.9.12. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34236384 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Regulatory Mechanism of CXCL16 Molecule-Related Antigen Presentation Using lncRNA-mRNA Co-Expression Network Analysis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Dec 24;17:11561-11575. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S496133. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39735899 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials