Identification of Prognostic Dosage-Sensitive Genes in Colorectal Cancer Based on Multi-Omics
- PMID: 31998369
- PMCID: PMC6962299
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01310
Identification of Prognostic Dosage-Sensitive Genes in Colorectal Cancer Based on Multi-Omics
Abstract
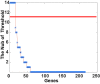
Several studies have already identified the prognostic markers in colorectal cancer (CRC) based on somatic copy number alteration (SCNA). However, very little information is available regarding their value as a prognostic marker. Gene dosage effect is one important mechanism of copy number and dosage-sensitive genes are more likely to behave like driver genes. In this work, we propose a new pipeline to identify the dosage-sensitive prognostic genes in CRC. The RNAseq data, the somatic copy number of CRC from TCGA were assayed to screen out the SCNAs. Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used to identify the differentially expressed genes in alteration samples with |SCNA| > 0.3. Cox-regression was used to find the candidate prognostic genes. An iterative algorithm was built to identify the stable prognostic genes. Finally, the Pearson correlation coefficient was calculated between gene expression and SCNA as the dosage effect score. The cell line data from CCLE was used to test the consistency of the dosage effect. The differential co-expression network was built to discover their function in CRC. A total of six amplified genes (NDUFB4, WDR5B, IQCB1, KPNA1, GTF2E1, and SEC22A) were found to be associated with poor prognosis. They demonstrate a stable prognostic classification in more than 50% threshold of SCNA. The average dosage effect score was 0.5918 ± 0.066, 0.5978 ± 0.082 in TCGA and CCLE, respectively. They also show great stability in different data sets. In the differential co-expression network, these six genes have the top degree and are connected to the driver and tumor suppressor genes. Function enrichment analysis revealed that gene NDUFB4 and GTF2E1 affect cancer-related functions such as transmembrane transport and transformation factors. In conclusion, the pipeline for identifying the prognostic dosage-sensitive genes in CRC was proved to be stable and reliable.
Keywords: colorectal cancer; differential co-expression; gene dosage effect; somatic copy number alteration; survival analysis.
Copyright © 2020 Chang, Miao and Zhao.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification and Characterization of the Copy Number Dosage-Sensitive Genes in Colorectal Cancer.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020 Jun 24;18:501-510. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2020.06.020. eCollection 2020 Sep 11. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020. PMID: 32775488 Free PMC article.
-
Survival marker genes of colorectal cancer derived from consistent transcriptomic profiling.BMC Genomics. 2018 Dec 11;19(Suppl 8):857. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5193-9. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30537927 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of biomarkers associated with diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer patients based on integrated bioinformatics analysis.Gene. 2019 Apr 15;692:119-125. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.01.001. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30654001
-
Identification and Characterization of MicroRNAs Associated with Somatic Copy Number Alterations in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Nov 29;10(12):475. doi: 10.3390/cancers10120475. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30501131 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Genes Related to Clinicopathological Characteristics and Prognosis of Patients with Colorectal Cancer.DNA Cell Biol. 2020 Apr;39(4):690-699. doi: 10.1089/dna.2019.5088. Epub 2020 Feb 6. DNA Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32027181
Cited by
-
Homologous Recombination Deficiency Is Associated with Shorter Survival in Colorectal Cancer Patients.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2025 Apr 22;56(1):105. doi: 10.1007/s12029-025-01231-x. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40261491
-
Screening of the differentially expressed proteins in malignant transformation of BEAS-2B cells induced by coal tar pitch extract.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023 Mar 13;12(2):270-281. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfad015. eCollection 2023 Apr. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023. PMID: 37125331 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of oxidative phosphorylation-related prognostic risk score model in uveal melanoma.BMC Ophthalmol. 2024 May 2;24(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s12886-024-03441-6. BMC Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38698303 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of nuclear export and import receptors in cancer and their potential in combination chemotherapy.IUBMB Life. 2024 Jan;76(1):4-25. doi: 10.1002/iub.2773. Epub 2023 Aug 25. IUBMB Life. 2024. PMID: 37623925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of IQCB1 in liver cancer: a bioinformatics analysis.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 30;13(9):5021-5036. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-110. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39430824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bae J. M., Wen X., Kim T. S., Kwak Y., Cho N. Y., Lee H. S., et al. (2019). Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) amplification detected by droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (ddPCR) is a prognostic factor in colorectal cancers. Cancer Res. Treat. 10.4143/crt.2019.062 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

