Analysis of Molecular Pretreated Tumor Profiles as Predictive Biomarkers of Therapeutic Response and Survival Outcomes after Neoadjuvant Therapy for Rectal Cancer in Moroccan Population
- PMID: 31998419
- PMCID: PMC6977322
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8459303
Analysis of Molecular Pretreated Tumor Profiles as Predictive Biomarkers of Therapeutic Response and Survival Outcomes after Neoadjuvant Therapy for Rectal Cancer in Moroccan Population
Abstract
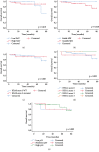
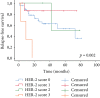
Pathologic features depending on tumor response to preoperative chemoradiotherapy are important to determine the outcomes in patients with rectal cancer. Evaluating the potential predictive roles of biomarker expression and their prognostic impact is a promising challenge. We reported here the immunohistochemical staining of a panel marker of mismatch repair protein (MMR), Ki67, HER-2, and p53. Additionally, identification of somatic mutations of KRAS, NRAS, and BRAF genes were performed by direct sequencing and pyrosequencing in pretreated biopsy tissues from 57 patients diagnosed for rectal cancer. Clinical features and pathological criteria for postneoadjuvant treatment surgical resection specimen's data were collected. Immunohistochemical expression and mutational status were correlated with therapeutic response, overall survival, and disease progression. The mean age of patients was 56 years. Seven (12.3%) out of 57 patients had a complete therapeutic response. Our analysis showed that when using complete therapeutic response (Dworak 4) and incomplete therapeutic response (Dworak 3, 2, and 1) as grouping factor, high p53 expression at the pretreatment biopsy was significantly associated to an incomplete response (p = 0.002). For 20 and 2 out of 57, KRAS and NRAS mutations were detected, respectively. The majority of these mutations affected codon 12. KRAS mutations detected at codon 146 (A146T, A146V) was associated with the appearance of recurrence and distant metastasis (p = 0.019). A high expression of HER-2 corresponding to score 3+ was observed in 3 pretreatment biopsy specimens. This class was significantly associated with a short relapse-free survival (p = 0.002). Furthermore, the high expression of Ki67 was moderately correlated with an older age (p = 0.016, r = 0.319). In addition, this shows that high p53 expression in the pretreatment biopsy was associated with an incomplete response in surgical resection specimens after neoadjuvant treatment, and a HER-2 score 3+ can be a predictive factor of distant metastasis and local recurrence. Larger, prospective, and more studies are needed.
Copyright © 2020 Ihsane El Otmani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Sauer R., Liersch T., Merkel S., et al. Preoperative versus postoperative chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer: results of the German CAO/ARO/AIO-94 randomized phase III trial after a median follow-up of 11 years. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2012;30(16):1926–1933. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.40.1836. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

