Ezetimibe Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation via the AMPK/Nrf2/TXNIP Pathway after MCAO in Rats
- PMID: 31998437
- PMCID: PMC6964721
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/4717258
Ezetimibe Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation via the AMPK/Nrf2/TXNIP Pathway after MCAO in Rats
Abstract
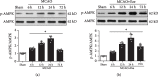
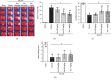
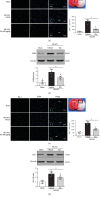
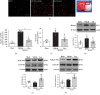
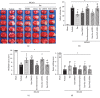
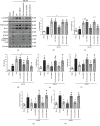
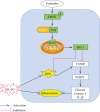
Oxidative stress and neuroinflammation play essential roles in ischemic stroke-induced brain injury. Previous studies have reported that Ezetimibe (Eze) exerts antioxidative stress and anti-inflammatory properties in hepatocytes. In the present study, we investigated the effects of Eze on oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in a rat middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model. One hundred and ninety-eight male Sprague-Dawley rats were used. Animals assigned to MCAO were given either Eze or its control. To explore the downstream signaling of Eze, the following interventions were given: AMPK inhibitor dorsomorphin and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) siRNA. Intranasal administration of Eze, 1 h post-MCAO, further increased the endogenous p-AMPK expression, reducing brain infarction, neurologic deficits, neutrophil infiltration, microglia/macrophage activation, number of dihydroethidium- (DHE-) positive cells, and malonaldehyde (MDA) levels. Specifically, treatment with Eze increased the expression of p-AMPK, Nrf2, and HO-1; Romo-1, thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP), NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3), Cleaved Caspase-1, and IL-1β were reduced. Dorsomorphin and Nrf2 siRNA reversed the protective effects of Eze. In summary, Eze decreases oxidative stress and subsequent neuroinflammation via activation of the AMPK/Nrf2/TXNIP pathway after MCAO in rats. Therefore, Eze may be a potential therapeutic approach for ischemic stroke patients.
Copyright © 2020 Jing Yu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Shen M. H., Zhang C. B., Zhang J. H., Li P. F. Electroacupuncture attenuates cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in middle cerebral artery occlusion of rat via modulation of apoptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, and excitotoxicity. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2016;2016:15. doi: 10.1155/2016/9438650.9438650 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

