Hydrogen sulfide improves vessel formation of the ischemic adductor muscle and wound healing in diabetic db/db mice
- PMID: 31998462
- PMCID: PMC6885384
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2019.36551.8709
Hydrogen sulfide improves vessel formation of the ischemic adductor muscle and wound healing in diabetic db/db mice
Abstract
Objectives: It has been demonstrated that hydrogen sulfide plays a vital role in physiological and pathological processes such as regulating inflammation, oxidative stress, and vessel relaxation. The aim of the study was to explore the effect of hydrogen sulfide on angiogenesis in the ischemic adductor muscles of type 2 diabetic db/db mice and ischemic diabetic wound healing.
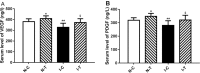
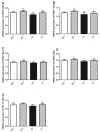
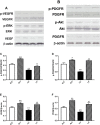
Materials and methods: The femoral arteries of diabetic db/db mice were isolated and ligated for preparation of ischemic hind limb model. Round incision was made on ischemic and non-ischemic limbs. The wounds were treated with sodium bisulfide (hydrogen sulfide donor). Real-time PCR and Western blotting were used to measure transcription of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF), platelet derived growth factor (PDGF), hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and protein expression of VEGF, VEGF receptor (VEGFR) and PDGF, PDGF receptor (PDGFR), respectively. Angiogenesis and morphological changes in adductor muscles were observed.
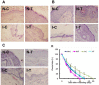
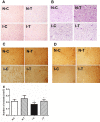
Results: Hydrogen sulfide significantly increased transcription of VEGF, EGF, PDGF, HIF-1α, eNOS and protein expression of VEGF, PDGF, and phosphorylated VEGFR and PDGFR. Treatment with hydrogen sulfide significantly improved ischemic wound healing and formation of granulation tissue, and increased the number of small vessels in the ischemic adductor muscles.
Conclusion: Our data suggested that hydrogen sulfide attenuated injury of ischemic adductor muscle, and promoted the ischemic diabetic wound healing via modulating angiogenesis in type 2 diabetic db/db mice.
Keywords: Adductor muscle Angiogenesis; Diabetes; Hydrogen sulfide; Ischemia; db/db mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gregg EW, Gu Q, Cheng YJ, Narayan KM, Cowie CC. Mortality trends in men and women with diabetes, 1971 to 2000. Ann Intern Med. 2007;147:149–155. - PubMed
-
- Dash SN, Dash NR, Guru B, Mohapatra PC. Towards reaching the target: clinical application of mesenchymal stem cells for diabetic foot ulcers. Rejuvenation Res. 2014;17:40–53. - PubMed
-
- Srikanth S, Deedwania P. Primary and secondary prevention strategy for cardiovascular disease in diabetes mellitus. Cardiol Clin. 2011;29:47–70. - PubMed
-
- Nathan DM, Genuth S, Lachin J, Cleary P, Crofford O, Davis M, et al. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:977–986. - PubMed
-
- Falanga V. Wound healing and its impairment in the diabetic foot. Lancet. 2005;366:1736–1743. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
