The Effects of Baduanjin Qigong on Postural Stability, Proprioception, and Symptoms of Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 31998728
- PMCID: PMC6966958
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00307
The Effects of Baduanjin Qigong on Postural Stability, Proprioception, and Symptoms of Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
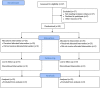
Background: Knee osteoarthritis is a common disease affecting a large number of old individuals worldwide. This study aimed to explore the effects of Baduanjin Qigong in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Methods: Fifty participants with knee osteoarthritis were randomly assigned to either an experimental group (n = 25) or a control group (n = 25). Participants in the experimental group received Baduanjin Qigong training for 12 weeks, with three sessions per week lasting 40 min per session. Participants in the control group did not receive any additional physical training. All of participants completed outcome (proprioception, postural stability, and functional ability) assessments at three time points (baseline, Week 8, 12). Results: Proprioception and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index function were statistically improved at eighth and 12th week of the intervention in the Baduanjin Qigong group (p < 0.05), while the control group did not have any significant changes. For postural stability at the anterior-posterior direction with eyes closed, Baduanjin Qigong group showed significant improvement compared to controls after the 12 weeks of intervention (p < 0.05). Conclusions: Regular Baduanjin Qigong practice helped the improvement of knee joint proprioception and postural stability, and reduction of pain, stiffness, and functional impairments of old adults with knee osteoarthritis. Well-designed randomized controlled trials with long-term assessment are needed. The trial was registered in Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR-IOR-16010042). URL: http://www.chictr.org.cn/hvshowproject.aspx?id=10550.
Keywords: Baduanjin; Qigong; exercise; mind-body exercise; osteoarthritis; postural stability; proprioception.
Copyright © 2020 Ye, Simpson, Liu, Lin, Zhong, Cai and Zou.
Figures
References
-
- Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. (2012) 380:2163–96. 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources