Direct targeting of oncogenic RAS mutants with a tumor-specific cytosol-penetrating antibody inhibits RAS mutant-driven tumor growth
- PMID: 31998840
- PMCID: PMC6962039
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aay2174
Direct targeting of oncogenic RAS mutants with a tumor-specific cytosol-penetrating antibody inhibits RAS mutant-driven tumor growth
Abstract
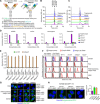
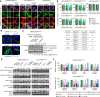
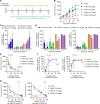
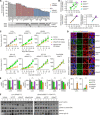
Oncogenic RAS mutant (RASMUT) proteins have been considered undruggable via conventional antibody regimens owing to the intracellular location restricting conventional-antibody accessibility. Here, we report a pan-RAS-targeting IgG antibody, inRas37, which directly targets the intracellularly activated form of various RASMUT subtypes after tumor cell-specific internalization into the cytosol to block the interactions with effector proteins, thereby suppressing the downstream signaling. Systemic administration of inRas37 exerted a potent antitumor activity in a subset of RASMUT tumor xenografts in mice, but little efficacy in RASMUT tumors with concurrent downstream PI3K mutations, which were overcome by combination with a PI3K inhibitor. The YAP1 protein was up-regulated as an adaptive resistance-inducing response to inRas37 in RASMUT-dependent colorectal tumors; accordingly, a combination of inRas37 with a YAP1 inhibitor manifested synergistic antitumor effects in vitro and in vivo. Our study offers a promising pan-RAS-targeting antibody and the corresponding therapeutic strategy against RASMUT tumors.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antibody targeting intracellular oncogenic Ras mutants exerts anti-tumour effects after systemic administration.Nat Commun. 2017 May 10;8:15090. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15090. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28489072 Free PMC article.
-
Specific inhibition of oncogenic RAS using cell-permeable RAS-binding domains.Cell Chem Biol. 2021 Nov 18;28(11):1581-1589.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2021.04.013. Epub 2021 May 7. Cell Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 33964212
-
Dual-targeting of EGFR and Neuropilin-1 attenuates resistance to EGFR-targeted antibody therapy in KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Lett. 2019 Dec 1;466:23-34. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.09.005. Epub 2019 Sep 12. Cancer Lett. 2019. PMID: 31521695
-
Past, Present, and Future of Targeting Ras for Cancer Therapies.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2016;16(5):345-57. doi: 10.2174/1389557515666151001154111. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26423695 Review.
-
Improving Prospects for Targeting RAS.J Clin Oncol. 2015 Nov 1;33(31):3650-9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.62.1052. Epub 2015 Sep 14. J Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26371146 Review.
Cited by
-
Improved intratumoral penetration of IL12 immunocytokine enhances the antitumor efficacy.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 27;13:1034774. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1034774. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36405748 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast Mating as a Tool for Highly Effective Discovery and Engineering of Antibodies via Display Methodologies.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2491:313-333. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2285-8_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35482198
-
Biology, pathology, and therapeutic targeting of RAS.Adv Cancer Res. 2020;148:69-146. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2020.05.002. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Adv Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32723567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic Therapy Improvements Will Render Locoregional Treatments Obsolete for Patients with Cancer with Liver Metastases.Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2021 Jan;30(1):189-204. doi: 10.1016/j.soc.2020.08.008. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2021. PMID: 33220805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Somatic gain-of-function mutations in BUD13 promote oncogenesis by disrupting Fbw7 function.J Exp Med. 2023 Oct 2;220(10):e20222056. doi: 10.1084/jem.20222056. Epub 2023 Jun 29. J Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37382881 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

