Chlamydomonas CHT7 Is Required for an Effective Quiescent State by Regulating Nutrient-Responsive Cell Cycle Gene Expression
- PMID: 32001503
- PMCID: PMC7145468
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.19.00628
Chlamydomonas CHT7 Is Required for an Effective Quiescent State by Regulating Nutrient-Responsive Cell Cycle Gene Expression
Abstract
COMPROMISED HYDROLYSIS OF TRIACYLGLYCEROLS7 (CHT7) in Chlamydomonas (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii) was previously shown to affect the transcription of a subset of genes during nitrogen (N)-replete growth and following N refeeding. Here, we show that an extensive derepression of genes involved in DNA metabolism and cell cycle-related processes, as well as downregulation of genes encoding oxidoreductases and nutrient transporters, occurs in the cht7 mutant during N deprivation. Cellular mutant phenotypes are consistent with the observed transcriptome misregulation, as cht7 cells fail to properly arrest growth, nuclear replication, and cell division following N deprivation. Reduction in cht7 colony formation following N refeeding is explained by its compromised viability during N deprivation and by the occurrence of abortive divisions during N refeeding. Surprisingly, the largely unstructured C-terminal half of CHT7 with predicted protein binding domains, but not the canonical CXC DNA binding domain, is essential for the ability of CHT7 to form stable complexes and reverse the cellular phenotypes and transcription levels in the cht7 mutant. Hence, although lacking the presumed DNA binding domain, CHT7 modulates the expression of cell cycle genes in response to N availability, which is essential for establishing an effective quiescent state and the coordinated resumption of growth following N refeeding.
© 2020 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved.
Figures
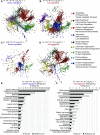


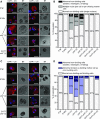

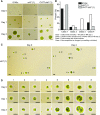
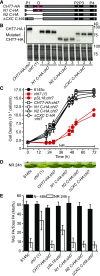

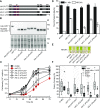
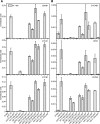



Comment in
-
When to Sleep? CHT7 Is Critical for Nutrient-Dependent Quiescence in Chlamydomonas.Plant Cell. 2020 Apr;32(4):810-811. doi: 10.1105/tpc.20.00069. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Plant Cell. 2020. PMID: 32024688 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Aoki K., Ogata Y., Shibata D.(2007). Approaches for extracting practical information from gene co-expression networks in plant biology. Plant Cell Physiol. 48: 381–390. - PubMed
-
- Beall E.L., Manak J.R., Zhou S., Bell M., Lipsick J.S., Botchan M.R.(2002). Role for a Drosophila Myb-containing protein complex in site-specific DNA replication. Nature 420: 833–837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

