Targeting of TLE3 by miR-3677 in human breast cancer promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion
- PMID: 32002031
- PMCID: PMC6960393
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.11241
Targeting of TLE3 by miR-3677 in human breast cancer promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion
Retraction in
-
[Retracted] Targeting of TLE3 by miR‑3677 in human breast cancer promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion.Oncol Lett. 2024 Dec 9;29(2):94. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14840. eCollection 2025 Feb. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39697980 Free PMC article.
Abstract
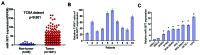
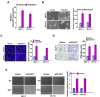
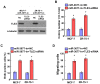
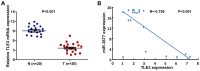
Numerous studies have indicated an important function of microRNAs (miRs) in breast cancer (BC) progression, oncogenesis and metastasis. However, the function of miR-3677, which has been revealed to be upregulated in BC [The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data], has not been investigated to date. In the present study, miR-3677 was revealed to be upregulated in BC as determined using TCGA. miR-3677 was significantly upregulated in BC tissues and cell lines compared with those noted in adjacent non-cancerous tissues and primary normal breast cells (P<0.05). The overexpression of miR-3677 promoted the cell proliferation, migration and invasion of BC cells. Using bioinformatics algorithms and luciferase assays, a novel target gene for miR-3677, namely transducin-like enhancer of Split3 (TLE3), was identified. Silencing of TLE3 in miR-3677-transfected BC cells suppressed their proliferation and migration. An inverse correlation was observed between miR-3677 and TLE3 expression levels in human BC tissues. In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that miR-3677 promoted BC cell proliferation, migration and invasion by inhibiting TLE3 expression, which provided a novel mechanism and a promising therapeutic target for patients with BC.
Keywords: breast cancer; cell metastasis; cell proliferation; microRNA-3677; transducin-like enhancer of Split3.
Copyright: © Peng et al.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
