Activated human astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles modulate neuronal uptake, differentiation and firing
- PMID: 32002171
- PMCID: PMC6968484
- DOI: 10.1080/20013078.2019.1706801
Activated human astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles modulate neuronal uptake, differentiation and firing
Abstract
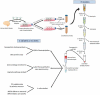
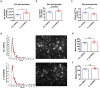
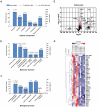
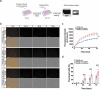
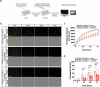
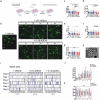
Astrocytes in the central nervous system (CNS) provide supportive neural functions and mediate inflammatory responses from microglia. Increasing evidence supports their critical roles in regulating brain homoeostasis in response to pro-inflammatory factors such as cytokines and pathogen/damage-associated molecular pattern molecules in infectious and neurodegenerative diseases. However, the underlying mechanisms of the trans-cellular communication are still unclear. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) can transfer a large diversity of molecules such as lipids, nucleic acids and proteins for cellular communications. The purpose of this study is to characterize the EVs cargo proteins derived from human primary astrocytes (ADEVs) under both physiological and pathophysiological conditions. ADEVs were isolated from human primary astrocytes after vehicle (CTL) or interleukin-1β (IL-1β) pre-treatment. Label-free quantitative proteomic profiling revealed a notable up-regulation of proteins including actin-associated molecules, integrins and major histocompatibility complex in IL-1β-ADEVs compared to CTL-ADEVs, which were involved in cellular metabolism and organization, cellular communication and inflammatory response. When fluorescently labelled ADEVs were added into primary cultured mouse cortical neurons, we found a significantly increased neuronal uptake of IL-1β-ADEVs compared to CTL-ADEVs. We further confirmed it is likely due to the enrichment of surface proteins in IL-1β-ADEVs, as IL-1β-ADEVs uptake by neurons was partially suppressed by a specific integrin inhibitor. Additionally, treatment of neurons with IL-1β-ADEVs also reduced neurite outgrowth, branching and neuronal firing. These findings provide insight for the molecular mechanism of the ADEVs' effects on neural uptake, neural differentiation and maturation, and its alteration in inflammatory conditions.
Keywords: Astrocytes; IL-1β; exosome; extracellular matrix; extracellular vesicles; inflammatory diseases; neurodegenerative diseases; proteomics.
© 2019 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group on behalf of The International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stimulus-dependent modifications in astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicle cargo regulate neuronal excitability.Glia. 2020 Jan;68(1):128-144. doi: 10.1002/glia.23708. Epub 2019 Aug 30. Glia. 2020. PMID: 31469478
-
TNFα and IL-1β modify the miRNA cargo of astrocyte shed extracellular vesicles to regulate neurotrophic signaling in neurons.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Mar 5;9(3):363. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0369-4. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29507357 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles: Neuroreparative properties and role in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders.J Control Release. 2020 Jul 10;323:225-239. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.04.017. Epub 2020 Apr 11. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32289328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicular NFIA mediates obesity-associated cognitive impairment.J Neuroinflammation. 2025 May 30;22(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03473-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2025. PMID: 40448146 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles (ADEVs): Deciphering their Influences in Aging.Aging Dis. 2021 Sep 1;12(6):1462-1475. doi: 10.14336/AD.2021.0608. eCollection 2021 Sep. Aging Dis. 2021. PMID: 34527422 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Their Renin-Angiotensin Cargo as a Link between Metabolic Syndrome and Parkinson's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Nov 26;12(12):2045. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122045. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136165 Free PMC article.
-
Natural cell based biomimetic cellular transformers for targeted therapy of digestive system cancer.Theranostics. 2022 Oct 9;12(16):7080-7107. doi: 10.7150/thno.75937. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36276645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating Extracellular Vesicles: Their Role in Patients with Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) Undergoing EndoVascular Aortic Repair (EVAR).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 16;23(24):16015. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416015. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555653 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles-Based Cell-Cell Communication in Melanoma: New Perspectives in Diagnostics and Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 4;24(2):965. doi: 10.3390/ijms24020965. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk of Astrocytes and Other Cells during Ischemic Stroke.Life (Basel). 2022 Jun 17;12(6):910. doi: 10.3390/life12060910. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35743941 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Colombo E, Farina C.. Astrocytes: key regulators of neuroinflammation. Trends Immunol. 2016;37(9):608–18. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

