Translation of two-photon microscopy to the clinic: multimodal multiphoton CARS tomography of in vivo human skin
- PMID: 32003191
- PMCID: PMC6991706
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JBO.25.1.014515
Translation of two-photon microscopy to the clinic: multimodal multiphoton CARS tomography of in vivo human skin
Abstract
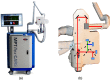
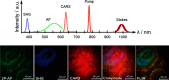
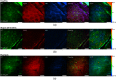
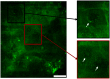
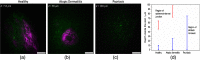
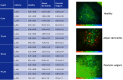
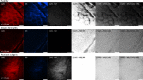
<p>Two-photon microscopes have been successfully translated into clinical imaging tools to obtain high-resolution optical biopsies for <italic>in vivo</italic> histology. We report on clinical multiphoton coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy (CARS) tomography based on two tunable ultrashort near-infrared laser beams for label-free <italic>in vivo</italic> multimodal skin imaging. The multiphoton biopsies were obtained with the compact tomograph "MPTflex-CARS" using a photonic crystal fiber, an optomechanical articulated arm, and a four-detector-360 deg measurement head. The multiphoton tomograph has been employed to patients in a hospital with diseased skin. The clinical study involved 16 subjects, 8 patients with atopic dermatitis, 4 patients with psoriasis vulgaris, and 4 volunteers served as control. Two-photon cellular autofluorescence lifetime, second harmonic generation (SHG) of collagen, and CARS of intratissue lipids/proteins have been detected with single-photon sensitivity, submicron spatial resolution, and picosecond temporal resolution. The most important signal was the autofluorescence from nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide [NAD(P)H]. The SHG signal from collagen was mainly used to detect the epidermal-dermal junction and to calculate the ratio elastin/collagen. The CARS/Raman signal provided add-on information. Based on this view on the disease-affected skin on a subcellular level, skin areas affected by dermatitis and by psoriasis could be clearly identified. Multimodal multiphoton tomographs may become important label-free clinical high-resolution imaging tools for <italic>in vivo</italic> skin histology to realize rapid early diagnosis as well as treatment control.</p>.
Keywords: coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy; femtosecond laser; fluorescence lifetime imaging; medical imaging; multiphoton tomography; second harmonic generation; skin; two-photon microscopy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
High-resolution multiphoton tomography of human skin with subcellular spatial resolution and picosecond time resolution.J Biomed Opt. 2003 Jul;8(3):432-9. doi: 10.1117/1.1577349. J Biomed Opt. 2003. PMID: 12880349
-
Combined in vivo multiphoton and CARS imaging of healthy and disease-affected human skin.Microsc Res Tech. 2012 Apr;75(4):492-8. doi: 10.1002/jemt.21082. Epub 2011 Oct 3. Microsc Res Tech. 2012. PMID: 21972128
-
Impact of refractive index mismatches on coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering and multiphoton autofluorescence tomography of human skin in vivo.Phys Med Biol. 2015 Sep 7;60(17):6881-99. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/60/17/6881. Epub 2015 Aug 25. Phys Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26305454
-
Review: Clinical in vivo multiphoton FLIM tomography.Methods Appl Fluoresc. 2020 Apr 22;8(3):034002. doi: 10.1088/2050-6120/ab8808. Methods Appl Fluoresc. 2020. PMID: 32320386 Review.
-
Two-photon microscopes and in vivo multiphoton tomographs--powerful diagnostic tools for tissue engineering and drug delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006 Sep 15;58(7):878-96. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2006.07.004. Epub 2006 Sep 28. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006. PMID: 17011064 Review.
Cited by
-
A 20 MHz Repetition Rate, Sub-Picosecond Ti-Sapphire Laser for Fiber Delivery in Nonlinear Microscopy of the Skin.Life (Basel). 2024 Feb 7;14(2):231. doi: 10.3390/life14020231. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38398740 Free PMC article.
-
Toward next-generation endoscopes integrating biomimetic video systems, nonlinear optical microscopy, and deep learning.Biophys Rev (Melville). 2023 Jun 29;4(2):021307. doi: 10.1063/5.0133027. eCollection 2023 Jun. Biophys Rev (Melville). 2023. PMID: 38510341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skin Barriers in Dermal Drug Delivery: Which Barriers Have to Be Overcome and How Can We Measure Them?Pharmaceutics. 2020 Jul 20;12(7):684. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12070684. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32698388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging and component analysis of pumpkin stem tissue with simultaneous SF-CARS and TPEF microscopy.Biomed Opt Express. 2023 Aug 24;14(9):4862-4874. doi: 10.1364/BOE.497260. eCollection 2023 Sep 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2023. PMID: 37791252 Free PMC article.
-
Label-free multiphoton microscopy enables histopathological assessment of colorectal liver metastases and supports automated classification of neoplastic tissue.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 15;13(1):4274. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31401-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36922643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Göppert M., “Über die Wahrscheinlichkeit des Zusammenwirkens zweier Lichtquanten in einem Elementarakt,” Die Naturwissenschaften 17, 932–932 (1929).10.1007/BF01506585 - DOI
-
- Göppert-Mayer M., “Über Elementarakte mit zwei Quantensprüngen,” Ann. Phys. 401, 273–294 (1931).ANPYA210.1002/andp.19314010303 - DOI
-
- Kaiser W., Garrett C. G. B., “Two-photon excitation in ,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 7, 229–231 (1961).PRLTAO10.1103/PhysRevLett.7.229 - DOI
-
- König K., Multiphoton Microscopy and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging, De Gruyter, Berlin and Boston, Open access (2018).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

