Association between carnitine deficiency and the erythropoietin resistance index in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis: a cross-sectional observational study
- PMID: 32003308
- PMCID: PMC7034042
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2020.1719847
Association between carnitine deficiency and the erythropoietin resistance index in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis: a cross-sectional observational study
Abstract
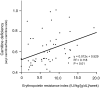
Carnitine deficiency contributes to developing various pathological conditions, such as cardiac dysfunction, muscle weakness, and erythropoietin-resistant anemia in patients undergoing hemodialysis. However, a conclusion has not been reached concerning the prevalence and the effect of carnitine deficiency in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis (PD). In this study, the prevalence of carnitine deficiency and the clinical factors associated with carnitine deficiency were investigated in 60 patients undergoing PD. The median age of the patients was 62.5 years (52.5-72.5 years), the proportion of male sex was 44/60 (73.3%), and the median PD period was 24 months (12-45 months). Carnitine deficiency (acyl carnitine/free carnitine ratio >0.4) was detected in 56/60 (93%) patients. Multiple regression analysis showed that the erythropoietin resistance index was independently associated with carnitine deficiency (β = 0.283, p = 0.04). These results suggest that carnitine plays pivotal roles in hematogenesis in patients undergoing PD.
Keywords: Anemia; carnitine deficiency; erythropoietin resistance index; peritoneal dialysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Yang SK, Xiao L, Song PA, et al. . Effect of L-carnitine therapy on patients in maintenance hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nephrol. 2014;27:317–329. - PubMed
-
- Kamei D, Tsuchiya K, Nitta K, et al. . Association between resistance to erythropoiesis-stimulating agents and carnitine profile in patients on maintenance haemodialysis. Nephrology (Carlton, Vic). 2018;23:737–743. - PubMed
-
- Schreiber BD. Debate forum: levocarnitine therapy is rational and justified in selected dialysis patients. Blood Purif. 2006;24:128–139. - PubMed
-
- Rebouche CJ, Engel AG.. Carnitine metabolism and deficiency syndromes. Mayo Clin Proc. 1983;58:533–540. - PubMed
-
- Naseri M, Mottaghi Moghadam Shahri H, Horri M, et al. . absolute and relative carnitine deficiency in patients on hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2016;10:36–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical