Eccentric and Isometric Exercises in Achilles Tendinopathy Evaluated by the VISA-A Score and Shear Wave Elastography
- PMID: 32003647
- PMCID: PMC7787566
- DOI: 10.1177/1941738119893996
Eccentric and Isometric Exercises in Achilles Tendinopathy Evaluated by the VISA-A Score and Shear Wave Elastography
Abstract
Background: Apart from eccentric exercises (EE), isometric exercises (ISO) might be a treatment option for Achilles tendinopathy. Shear wave elastography (SWE) provides information for diagnosis and for monitoring tissue elasticity, which is altered in symptomatic tendons.
Hypothesis: Isometric exercises will have a beneficial effect on patients' outcome scores. Based on SWE, insertional and midportion tendon parts will differ in their elastic properties according to current symptoms.
Study design: Randomized clinical trial.
Level of evidence: Level 2.
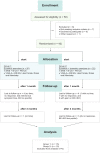
Methods: Group 1 (EE; n = 20; 12 males, 8 females; mean age, 52 ± 8.98 years) and group 2 (EE + ISO; n = 22; 15 males, 7 females; mean age, 47 ± 15.11 years) performed exercises for 3 months. Measurement points were before exercises were initiated as well as after 1 and 3 months using the Victorian Institute of Sports Assessment-Achilles (VISA-A) score, American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society score, and SWE (insertion and midportion).
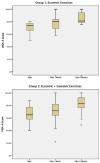
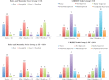
Results: Both groups improved significantly, but there were no significant interindividual differences (VISA-A; P = 0.362) between group 1 (n = 15; +15 VISA-A) and group 2 (n = 15; +15 VISA-A). The symptomatic insertion (symptomatic, 136.89 kPa; asymptomatic, 174.68 kPa; P = 0.045) and the symptomatic midportion of the Achilles tendon (symptomatic, 184.40 kPa; asymptomatic, 215.41 kPa; P = 0.039) had significantly lower Young modulus compared with the asymptomatic tendons. The midportion location had significantly higher Young modulus than the insertional part of the tendon (P = 0.005).
Conclusion: Isometric exercises do not have additional benefit when combined with eccentric exercises, as assessed over a 3-month intervention period. SWE is able to distinguish between insertional and midportion tendon parts in a symptomatic and asymptomatic state.
Clinical relevance: The present study shows no additional effect of ISO when added to baseline EE in treating Achilles tendinopathy. Different elastic properties of the insertional and midportion tendon have to be taken into consideration when rating a tendon as pathologic.
Keywords: Achilles tendinopathy; eccentric exercises; isometric exercises; muscle; shear wave elastography; tendon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no potential conflicts of interest in the development and publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Alfredson H, Pietilä T, Jonsson P, Lorentzon R. Heavy-load eccentric calf muscle training for the treatment of chronic Achilles tendinosis. Am J Sports Med. 1998;26:360-366. - PubMed
-
- Attia M, Scott A, Carpentier G, et al. Greater glycosaminoglycan content in human patellar tendon biopsies is associated with more pain and a lower VISA score. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48:469-475. - PubMed
-
- Babault N, Pousson M, Ballay Y, Van Hoecke J. Activation of human quadriceps femoris during isometric, concentric, and eccentric contractions. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2001;91:2628-2634. - PubMed
-
- Bakkegaard M, Johannsen FE, Højgaard B, Langberg H. Ultrasonography as a prognostic and objective parameter in Achilles tendinopathy: a prospective observational study. Eur J Radiol. 2015;84:458-462. - PubMed
-
- Dirrichs T, Quack V, Gatz M, Tingart M, Kuhl CK, Schrading S. Shear wave elastography (SWE) for the evaluation of patients with tendinopathies. Acad Radiol. 2016;23:1204-1213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

