Genetic polymorphism in C3 is associated with progression in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients with IgA nephropathy but not in other causes of CKD
- PMID: 32004338
- PMCID: PMC6994105
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228101
Genetic polymorphism in C3 is associated with progression in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients with IgA nephropathy but not in other causes of CKD
Abstract
Objectives: The R102G variant in complement 3 (C3) results in two allotypic variants: C3 fast (C3F) and C3 slow (C3S). C3F presents at increased frequency in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), our aim is to explore its role in CKD progression and mortality.
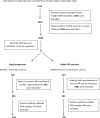
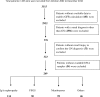
Methods: Delta (Δ) eGFR for 2038 patients in the Salford Kidney Study (SKS) was calculated by linear regression; those with ≤-3ml/min/1.73m2/yr were defined as rapid progressors (RP) and those with ΔeGFR between -0.5 and +1ml/min/1.73m2/yr, labelled stable CKD patients (SP).A group of 454 volunteers was used as a control group. In addition, all biopsy-proven glomerulonephritis (GN) patients were studied regardless of their ΔeGFR. R102G was analysed by real-time PCR, and genotypic and allelic frequencies were compared between RP and SP along with the healthy control group.
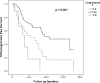
Results: There were 255 SP and 259 RP in the final cohort. Median ΔeGFR was 0.07 vs. -4.7 ml/min/1.73m2/yr in SP vs. RP. C3F allele frequency was found to be significantly higher in our CKD cohort (25.7%) compared with the healthy control group (20.6%); p = 0.008.However, there was no significant difference in C3F allele frequency between the RP and SP groups. In a subgroup analysis of 37 patients with IgA nephropathy in the CKD cohort (21 RP and 16 SP), there was a significantly higher frequency of C3F in RP 40.5% vs. 9.4% in SP; p = 0.003. In the GN group, Cox regression showed an association between C3F and progression only in those with IgA nephropathy (n = 114);HR = 1.9 (95% CI 1.1-3.1; p = 0.018) for individuals heterozygous for the C3F variant, increased further for individuals homozygous for the variant, HR = 2.8 (95% CI 1.2-6.2; p = 0.014).
Conclusion: The C3 variant R102G is associated with progression of CKD in patients with IgA nephropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma Galactose-Deficient IgA1 and C3 and CKD Progression in IgA Nephropathy.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Oct 7;14(10):1458-1465. doi: 10.2215/CJN.13711118. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31511226 Free PMC article.
-
The difference between human C3F and C3S results from a single amino acid change from an asparagine to an aspartate residue at position 1216 on the alpha-chain of the complement component, C3.J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1254-8. J Immunol. 1989. PMID: 2473125
-
Molecular analysis of C3 allotypes in patients with systemic vasculitis.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1994;9(11):1564-7. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1994. PMID: 7870343
-
Molecular analysis of C3 allotypes in Chinese patients with immunoglobulin A nephropathy.Am J Kidney Dis. 1994 Apr;23(4):543-6. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(12)80376-3. Am J Kidney Dis. 1994. PMID: 8154490
-
Complement C3 and its polymorphism: biological and clinical consequences.Pathology. 2014 Jan;46(1):1-10. doi: 10.1097/PAT.0000000000000042. Pathology. 2014. PMID: 24300728 Review.
Cited by
-
Network-based transcriptomic analysis identifies the genetic effect of COVID-19 to chronic kidney disease patients: A bioinformatics approach.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021 Oct;28(10):5647-5656. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.06.015. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34127904 Free PMC article.
-
A Study on Associations of Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR Polymorphisms With Genetic Susceptibility to Chronic Kidney Disease.J Clin Lab Anal. 2024 Jun;38(11-12):e25086. doi: 10.1002/jcla.25086. Epub 2024 Jul 3. J Clin Lab Anal. 2024. PMID: 38958113 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic signature associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD) progression identified by data-independent acquisition mass spectrometry.Clin Proteomics. 2023 Apr 20;20(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12014-023-09405-0. Clin Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 37076799 Free PMC article.
-
Complement activation in IgA nephropathy.Semin Immunopathol. 2021 Oct;43(5):679-690. doi: 10.1007/s00281-021-00882-9. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Semin Immunopathol. 2021. PMID: 34379175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mucosal Immune Defence Gene Polymorphisms as Relevant Players in the Pathogenesis of IgA Vasculitis?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 22;24(17):13063. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713063. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37685869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collins AJ, Foley RN, Gilbertson DT, Chen SC. The state of chronic kidney disease, ESRD, and morbidity and mortality in the first year of dialysis. Clin J Am SocNephrol. 2009;4 Suppl1:S5–11. - PubMed
-
- Eftimovska N, Stojceva-Taneva O, Polenakovic M. Slow progression of chronic kidney disease and what it is associated with. Prilozi. 2008;29:153–65. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous