Evaluation of the CareStart™ glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) rapid diagnostic test in the field settings and assessment of perceived risk from primaquine at the community level in Cambodia
- PMID: 32004348
- PMCID: PMC6994100
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228207
Evaluation of the CareStart™ glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) rapid diagnostic test in the field settings and assessment of perceived risk from primaquine at the community level in Cambodia
Abstract
Background: Primaquine is an approved radical cure treatment for Plasmodium vivax malaria but treatment can result in life-threatening hemolysis if given to a glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficient (G6PDd) patient. There is a need for reliable point-of-care G6PD diagnostic tests.
Objectives: To evaluate the performance of the CareStart™ rapid diagnostic test (RDT) in the hands of healthcare workers (HCWs) and village malaria workers (VMWs) in field settings, and to better understand user perceptions about the risks and benefits of PQ treatment guided by RDT results.
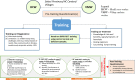
Methods: This study enrolled 105 HCWs and VMWs, herein referred to as trainees, who tested 1,543 healthy adult male volunteers from 84 villages in Cambodia. The trainees were instructed on G6PD screening, primaquine case management, and completed pre and post-training questionnaires. Each trainee tested up to 16 volunteers in the field under observation by the study staff.
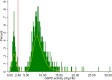
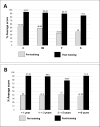
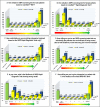
Results: Out of 1,542 evaluable G6PD volunteers, 251 (16.28%) had quantitative enzymatic activity less than 30% of an adjusted male median (8.30 U/g Hb). There was no significant difference in test sensitivity in detecting G6PDd between trainees (97.21%), expert study staff in the field (98.01%), and in a laboratory setting (95.62%) (p = 0.229); however, test specificity was different for trainees (96.62%), expert study staff in the field (98.14%), and experts in the laboratory (98.99%) (p < 0.001). Negative predictive values were not statistically different for trainees, expert staff, and laboratory testing: 99.44%, 99.61%, and 99.15%, respectively. Knowledge scores increased significantly post-training, with 98.7% willing to prescribe primaquine for P.vivax malaria, an improvement from 40.6% pre-training (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: This study demonstrated ability of medical staff with different background to accurately use CareStart™ RDT to identify G6PDd in male patients, which may enable safer prescribing of primaquine; however, pharmacovigilance is required to address possible G6PDd misclassifications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Population Reference Bureau (PRB). Fewer Malaria Cases in Cambodia. 2016 [12 JAN 2019]. Available from: http://www.prb.org/Publications/Articles/2002/FewerMalariaCasesinCambodi....
-
- Presidential Malaria Initiative. Fighting Malaria and Saving Lives: Operational Research. 2016. Available from: https://www.pmi.gov/how-we-work/cross-cutting-technical-areas/operationa....
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Control and elimination of Plasmodium vivax malaria–A technical brief. Geneva. 2015 [12 JAN 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/9789241509244/en/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

