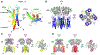
AMPA receptor structure and auxiliary subunits
- PMID: 32004381
- PMCID: PMC7392800
- DOI: 10.1113/JP278701
AMPA receptor structure and auxiliary subunits
Abstract
Fast excitatory synaptic transmission in the mammalian brain is largely mediated by AMPA-type ionotropic glutamate receptors (AMPARs), which are activated by the neurotransmitter glutamate. In synapses, the function of AMPARs is tuned by their auxiliary subunits, a diverse set of membrane proteins associated with the core pore-forming subunits of the AMPARs. Each auxiliary subunit provides distinct functional modulation of AMPARs, ranging from regulation of trafficking to shaping ion channel gating kinetics. Understanding the molecular mechanism of the function of these complexes is key to decoding synaptic modulation and their global roles in cognitive activities, such as learning and memory. Here, we review the structural and molecular complexity of AMPAR-auxiliary subunit complexes, as well as their functional diversity in different brain regions. We suggest that the recent structural information provides new insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying synaptic functions of AMPAR-auxiliary subunit complexes.
Keywords: AMPA receptors; AMPA type glutamate receptors; CKAMP44; GSG1L; Shisa; SynDIG; TARP; auxiliary subunits; cornichon; cryo-electron microscopy; electrophysiology; ion channel; ion channel gating modulation; ionotropic glutamate receptors; stargazin; structural biology; synaptic plasticity; synaptic transmission.
© 2020 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2020 The Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
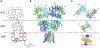
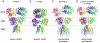
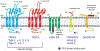

References
-
- Armstrong N & Gouaux E. (2000). Mechanisms for activation and antagonism of an AMPA-sensitive glutamate receptor: crystal structures of the GluR2 ligand binding core. Neuron 28, 165–181. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong N, Sun Y, Chen GQ & Gouaux E. (1998). Structure of a glutamate-receptor ligand-binding core in complex with kainate. Nature 395, 913–917. - PubMed
-
- Ayalon G & Stern-Bach Y. (2001). Functional assembly of AMPA and kainate receptors is mediated by several discrete protein-protein interactions. Neuron 31, 103–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

