Safety of endoscopic procedures with monopolar versus bipolar instruments in an ex vivo porcine model
- PMID: 32005163
- PMCID: PMC6995232
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-020-1176-9
Safety of endoscopic procedures with monopolar versus bipolar instruments in an ex vivo porcine model
Abstract
Background: Monopolar instruments are generally used in colorectal endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR). Bipolar instruments have previously been reported to be as safe as monopolar instruments. We sought to compare the safety of the monopolar and bipolar snare and hemostatic forceps in an animal model.
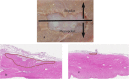
Methods: We created 5-mm, 10-mm, and 15-mm target lesions on an ex vivo porcine rectum. Two lesions of each size were resected via monopolar polypectomy (M-P), monopolar EMR (M-E), bipolar polypectomy (B-P), and bipolar EMR (B-E). We performed a pathological evaluation of the conditions of perforation and the effects of burning on the tissues. In addition, we burned the muscularis propria covered with submucosal layer using monopolar and bipolar hemostatic forceps and performed pathological evaluations.
Results: Polypectomy and EMR were performed in a total of 24 target lesions. A perforation was found on histology in one case of M-P and one case of M-E after removing target lesions of 15 mm in diameter. There were no perforations during endoscopic resection using the bipolar snare. The thermal denaturation in B-P did not reach the muscularis propria layer regardless of the size of the target lesion. Although thermal damage after using monopolar hemostatic forceps was extensive, thermal denaturation was only seen on the surface of the submucosal layer when bipolar hemostatic forceps were used.
Conclusions: Bipolar instruments cause less damage to the tissue than monopolar instruments. Our results also suggest that bipolar instruments may be safer than monopolar instruments in endoscopic procedures for colorectal lesions.
Keywords: Bipolar instrument; Colorectal endoscopic resection; Monopolar instrument.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

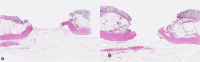

Similar articles
-
Hot snare polypectomy vs endoscopic mucosal resection using bipolar snare for intermediate size colorectal lesions: Propensity score matching.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Jun 21;29(23):3668-3677. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i23.3668. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37398881 Free PMC article.
-
Colorectal polypectomy and endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR): European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline.Endoscopy. 2017 Mar;49(3):270-297. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-102569. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Endoscopy. 2017. PMID: 28212588
-
Submucosal endoscopy with mucosal resection: a hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection in the porcine rectum and distal colon.Gastrointest Endosc. 2012 Oct;76(4):829-34. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2012.05.037. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012. PMID: 22854058
-
Complications of endoscopic polypectomy, endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection in the colon.Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2016 Oct;30(5):749-767. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2016.09.009. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27931634 Review.
-
AGA Institute Clinical Practice Update: Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in the United States.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jan;17(1):16-25.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.07.041. Epub 2018 Aug 2. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30077787 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of a new method, "non-injection resection using bipolar soft coagulation mode (NIRBS)", for colonic adenomatous lesions.Clin Endosc. 2023 Sep;56(5):623-632. doi: 10.5946/ce.2022.200. Epub 2023 May 18. Clin Endosc. 2023. PMID: 37524565 Free PMC article.
-
Radiofrequency Chondroplasty of the Knee Yields Excellent Clinical Outcomes and Minimal Complications: A Systematic Review.Arthrosc Sports Med Rehabil. 2023 Jul 17;5(4):100749. doi: 10.1016/j.asmr.2023.05.006. eCollection 2023 Aug. Arthrosc Sports Med Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 37520504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A method of "Noninjecting Resection using Bipolar Soft coagulation mode; NIRBS" for superficial non-ampullary duodenal epithelial tumor: a pilot study.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Oct 1;24(1):343. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03439-w. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39354393 Free PMC article.
-
Novel clip device for prevention of bleeding after endoscopic papillectomy.DEN Open. 2021 Sep 29;2(1):e51. doi: 10.1002/deo2.51. eCollection 2022 Apr. DEN Open. 2021. PMID: 35310706 Free PMC article.
-
New chapter in precision medicine: strategies for endoscopic resection of 10-20 mm non-pedunculated colorectal polyps.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025 May 8;18:17562848251338672. doi: 10.1177/17562848251338672. eCollection 2025. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40351382 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

