Methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MECP2) mutation type is associated with bone disease severity in Rett syndrome
- PMID: 32005172
- PMCID: PMC6995101
- DOI: 10.1186/s12881-020-0960-2
Methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MECP2) mutation type is associated with bone disease severity in Rett syndrome
Abstract
Background: More than 95% of individuals with RTT have mutations in methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MECP2), whose protein product modulates gene transcription. The disorder is caused by mutations in a single gene and the disease severity in affected individuals can be quite variable. Specific MECP2 mutations may lead phenotypic variability and different degrees of disease severity. It is known that low bone mass is a frequent and early complication of subjects with Rett syndrome. As a consequence of the low bone mass Rett girls are at an increased risk of fragility fractures. This study aimed to investigate if specific MECP2 mutations may affects the degree of involvement of the bone status in Rett subjects.
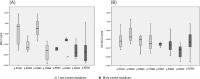
Methods: In 232 women with Rett syndrome (mean age 13.8 ± 8.3 yrs) we measured bone mineral density at whole body and at femur (BMD-FN and BMD-TH) by using a DXA machine (Hologic QDR 4500). QUS parameters were assessed at phalanxes by Bone Profiler-IGEA (amplitude dependent speed of sound: AD-SoS and bone transmission time: BTT). Moreover, ambulation capacity (independent or assisted), fracture history and presence of scoliosis were assessed. We divided the subjects with the most common point mutations in two group based on genotype-phenotype severity; in particular, there has been consensus in recognising that the mutations R106T, R168X, R255X, R270X are considered more severe.
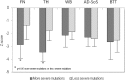
Results: As aspect, BMD-WB, BMD-FN and BMD-TH were lower in subjects with Rett syndrome that present the most severe mutations with respect to subjects with Rett syndrome with less severe mutations, but the difference was statistically significant only for BMD-FN and BMD-TH (p < 0.05). Also both AD-SoS and BTT values were lower in subjects that present the most severe mutations with respect to less severe mutations but the difference was not statistically significant. Moreover, subjects with Rett syndrome with more severe mutations present a higher prevalence of scoliosis (p < 0.05) and of inability to walk (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: This study confirms that MECP2 mutation type is a strong predictor of disease severity in subjects with Rett syndrome. In particular, the subjects with more severe mutation present a greater deterioration of bone status, and a higher prevalence of scoliosis and inability to walk.
Keywords: Fractures; Methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MECP2); Mutation severity; Osteoporosis; Rett syndrome; Scoliosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

