PDAC-ANN: an artificial neural network to predict pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on gene expression
- PMID: 32005189
- PMCID: PMC6995241
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-6533-0
PDAC-ANN: an artificial neural network to predict pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on gene expression
Abstract
Background: Although the pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) presents high mortality and metastatic potential, there is a lack of effective therapies and a low survival rate for this disease. This PDAC scenario urges new strategies for diagnosis, drug targets, and treatment.
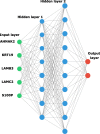
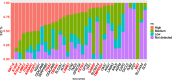
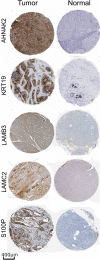
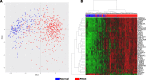
Methods: We performed a gene expression microarray meta-analysis of the tumor against normal tissues in order to identify differentially expressed genes (DEG) shared among all datasets, named core-genes (CG). We confirmed the CG protein expression in pancreatic tissue through The Human Protein Atlas. It was selected five genes with the highest area under the curve (AUC) among these proteins with expression confirmed in the tumor group to train an artificial neural network (ANN) to classify samples.
Results: This microarray included 461 tumor and 187 normal samples. We identified a CG composed of 40 genes, 39 upregulated, and one downregulated. The upregulated CG included proteins and extracellular matrix receptors linked to actin cytoskeleton reorganization. With the Human Protein Atlas, we verified that fourteen genes of the CG are translated, with high or medium expression in most of the pancreatic tumor samples. To train our ANN, we selected the best genes (AHNAK2, KRT19, LAMB3, LAMC2, and S100P) to classify the samples based on AUC using mRNA expression. The network classified tumor samples with an f1-score of 0.83 for the normal samples and 0.88 for the PDAC samples, with an average of 0.86. The PDAC-ANN could classify the test samples with a sensitivity of 87.6 and specificity of 83.1.
Conclusion: The gene expression meta-analysis and confirmation of the protein expression allow us to select five genes highly expressed PDAC samples. We could build a python script to classify the samples based on RNA expression. This software can be useful in the PDAC diagnosis.
Keywords: Artificial neural network; Meta-analysis; Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of differentially expressed genes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and normal pancreatic tissues based on microarray datasets.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Aug;20(2):1901-1914. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10414. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31257501
-
Identification of hub genes and regulators associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on integrated gene expression profile analysis.Discov Med. 2019 Sep;28(153):159-172. Discov Med. 2019. PMID: 31926587
-
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis reveals key genes involved in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma development.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2016 Aug;39(4):379-88. doi: 10.1007/s13402-016-0283-7. Epub 2016 May 30. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2016. PMID: 27240826
-
Gene signature and connectivity mapping to assist with drug prediction for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Surg Oncol. 2022 Sep;44:101849. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2022.101849. Epub 2022 Sep 11. Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36116415
-
Investigating the function and targeting of MET protein as an oncogene kinase in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A microarray data integration.Bioimpacts. 2024 Oct 1;15:30187. doi: 10.34172/bi.30187. eCollection 2025. Bioimpacts. 2024. PMID: 40161938 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Obscure Potential of AHNAK2.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 21;14(3):528. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030528. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of tumor targets selected from public genomic databases for imaging of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Sci Rep. 2025 May 16;15(1):17102. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00517-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40379788 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence assisted whole organ pancreatic fat estimation on magnetic resonance imaging and correlation with pancreas attenuation on computed tomography.Pancreatology. 2023 Aug;23(5):556-562. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2023.04.008. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Pancreatology. 2023. PMID: 37193618 Free PMC article.
-
Topographic analysis of pancreatic cancer by TMA and digital spatial profiling reveals biological complexity with potential therapeutic implications.Sci Rep. 2024 May 18;14(1):11361. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62031-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38762572 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using artificial intelligence analysis of pre-diagnostic computed tomography images.Cancer Biomark. 2022;33(2):211-217. doi: 10.3233/CBM-210273. Cancer Biomark. 2022. PMID: 35213359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilentz RE, Geradts J, Maynard R, Offerhaus GJ, Kang M, Goggins M, et al. Inactivation of the p16 (INK4A) tumor-suppressor gene in pancreatic duct lesions: loss of intranuclear expression. Cancer Res. 1998;58:4740–4744. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

