Effects of a quasi-experimental study of using flipped classroom approach to teach evidence-based medicine to medical technology students
- PMID: 32005227
- PMCID: PMC6995213
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-020-1946-7
Effects of a quasi-experimental study of using flipped classroom approach to teach evidence-based medicine to medical technology students
Abstract
Background: Flipped classroom is known to improve learning efficiency and to develop one's ability to apply high-level knowledge. To investigate the effect of flipped classroom approach on teaching evidence-based medicine to medical technology students, we conducted a tailor-made six flipped classroom based EBM courses for medical technology students.
Methods: This study adopted a qusai-experimental design with 62 medical technology interns as the research object. Students in the experimental group attended the flipped classroom course, while students in the control group attended the traditional course. The learning outcomes were evaluated by Fresno test in both groups. Furthermore, to understand student's perceptions on the flipped classroom approach, students in the experimental group were required to fill in a satisfaction survey and answer some open-ended questions.
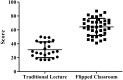
Results: The Fresno test scores of the experimental group were significantly higher than that of the control group. From the results of the satisfaction survey, we know that students were satisfied with this course format. Students claimed that the flipped classroom approach could improve their learning efficiency and the interactions with teacher could help them to think more deeply.
Conclusions: To conclude, most students showed positive attitudes and views on flipped classroom strategy. Moreover, students' questions were solved more effectively during class resulting in an improvement of effectiveness of evidence-based medicine trainings.
Keywords: Evidence-based medicine; Flipped classroom; Fresno test; Medical technology; Quasi-experiment; eBook.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Rosenberg W, Richardson WS, Sackett DL, Strauss SE, Haynes RB. Evidence-based medicine: how to practice and teach EBM: Churchill Livingstone. 2000.
-
- Knebel E, Greiner AC. Health professions education: a bridge to quality: National Academies Press. 2003. - PubMed
-
- Djulbegovic B, Guyatt GH. Progress in evidence-based medicine: a quarter century on. Lancet. 2017;390(10092):415–423. - PubMed
-
- McGinn T, Seltz M, Korenstein D. A method for real-time, evidence-based general medical attending rounds. Acad Med. 2002;77(11):1150–1152. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources