Myeloid-derived suppressor cells-new and exciting players in lung cancer
- PMID: 32005273
- PMCID: PMC6995114
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-020-0843-1
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells-new and exciting players in lung cancer
Abstract
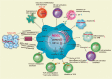
Lung cancer (LC) is the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide due to its late diagnosis and poor outcomes. As has been found for other types of tumors, there is increasing evidence that myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) play important roles in the promotion and progression of LC. Here, we briefly introduce the definition of MDSCs and their immunosuppressive functions. We next specifically discuss the multiple roles of MDSCs in the lung tumor microenvironment, including those in tumor growth and progression mediated by inhibiting antitumor immunity, and the associations of MDSCs with a poor prognosis and increased resistance to chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Finally, we also discuss preclinical and clinical treatment strategies targeting MDSCs, which may have the potential to enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Keywords: Anticancer; Immunosuppression; Lung cancer; MDSCs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Milette S, Fiset PO, Walsh LA, Spicer JD, Quail DF. The innate immune architecture of lung tumors and its implication in disease progression. J Pathol. 2019;247(5):589–605. - PubMed
-
- Adah D, Hussain M, Qin L, Qin L, Zhang J, Chen X. Implications of MDSCs-targeting in lung cancer chemo-immunotherapeutics. Pharmacol Res. 2016;110:25–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

