Muscarinic Modulation of SK2-Type K+ Channels Promotes Intrinsic Plasticity in L2/3 Pyramidal Neurons of the Mouse Primary Somatosensory Cortex
- PMID: 32005752
- PMCID: PMC7294454
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0453-19.2020
Muscarinic Modulation of SK2-Type K+ Channels Promotes Intrinsic Plasticity in L2/3 Pyramidal Neurons of the Mouse Primary Somatosensory Cortex
Abstract
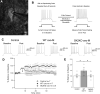
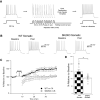
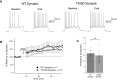
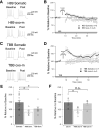
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) inhibit small-conductance calcium-activated K+ channels (SK channels) and enhance synaptic weight via this mechanism. SK channels are also involved in activity-dependent plasticity of membrane excitability ("intrinsic plasticity"). Here, we investigate whether mAChR activation can drive SK channel-dependent intrinsic plasticity in L2/3 cortical pyramidal neurons. Using whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from these neurons in slices prepared from mouse primary somatosensory cortex (S1), we find that brief bath application of the mAChR agonist oxotremorine-m (oxo-m) causes long-term enhancement of excitability in wild-type mice that is not observed in mice deficient of SK channels of the SK2 isoform. Similarly, repeated injection of depolarizing current pulses into the soma triggers intrinsic plasticity that is absent from SK2 null mice. Intrinsic plasticity lowers spike frequency adaptation and attenuation of spike firing upon prolonged activation, consistent with SK channel modulation. Depolarization-induced plasticity is prevented by bath application of the protein kinase A (PKA) inhibitor H89, and the casein kinase 2 (CK2) inhibitor TBB, respectively. These findings point toward a recruitment of two known signaling pathways in SK2 regulation: SK channel trafficking (PKA) and reduction of the calcium sensitivity (CK2). Using mice with an inactivation of CaMKII (T305D mice), we show that intrinsic plasticity does not require CaMKII. Finally, we demonstrate that repeated injection of depolarizing pulses in the presence of oxo-m causes intrinsic plasticity that surpasses the plasticity amplitude reached by either manipulation alone. Our findings show that muscarinic activation enhances membrane excitability in L2/3 pyramidal neurons via a downregulation of SK2 channels.
Keywords: engram; ensemble; excitability; learning; neocortex; pyramidal cell.
Copyright © 2020 Gill and Hansel.
Figures
References
-
- Belmeguenai A, Hosy E, Bengtsson F, Pedroarena CM, Piochon C, Teuling E, He Q, Ohtsuki G, De Jeu MT, Elgersma Y, De Zeeuw CI, Jörntell H, Hansel C (2010) Intrinsic plasticity complements long-term potentiation in parallel fiber input gain control in cerebellar Purkinje cells. J Neurosci 30:13630–13643. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3226-10.2010 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
