Intraarticular injection of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhances regeneration in knee osteoarthritis
- PMID: 32006075
- PMCID: PMC7669782
- DOI: 10.1007/s00167-020-05859-z
Intraarticular injection of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhances regeneration in knee osteoarthritis
Abstract
Purpose: This review aimed to evaluate the efficacy of intra-articular injections of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis (KOA).
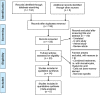
Methods: This narrative review evaluates recent English language clinical data and published research articles between 2014 and 2019. Key word search strings of ((("bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell" OR "bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cell" OR "bone marrow stromal cell")) AND ("osteoarthritis" OR "knee osteoarthritis")) AND ("human" OR "clinical"))) AND "intra-articular injection" were used to identify relevant articles using PMC, Cochrane Library, Web Of Science and Scopus databases.
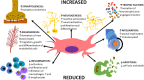
Results: Pre-clinical studies have demonstrated successful, safe and encouraging results for articular cartilage repair and regeneration. This is concluded to be due to the multilineage differential potential, immunosuppressive and self-renewal capabilities of BM-MSCs, which have shown to augment pain and improve functional outcomes. Subsequently, clinical applications of intra-articular injections of BM-MSCs are steadily increasing, with most studies demonstrating a decrease in poor cartilage index, improvements in pain, function and Quality of Life (QoL); with moderate-to-high level evidence regarding safety for therapeutic administration. However, low confidence in clinical efficacy remains due to a plethora of heterogenous methodologies utilised, resulting in challenging study comparisons. A moderate number of cells (40 × 106) were identified as most likely to achieve optimal responses in individuals with grade ≥ 2 KOA. Likewise, significant improvements were reported when using lower (24 × 106) and higher (100 × 106) cell numbers, although adverse effects including persistent pain and swelling were a consequence.
Conclusion: Overall, the benefits of intra-articular injections of BM-MSCs were deemed to outweigh the adverse effects; thus, this treatment be considered as a future therapy strategy. To realise this, long-term large-scale randomised clinical trials are required to enable improved interpretations, to determine the validity of efficacy in future studies.
Level of evidence: IV.
Keywords: Allogenic; Autologous; Cell therapies; Clinical efficacy; Immunomodulation; Mesenchymal stem cells; Optimal dosage; Osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. There is no funding to report related to the production of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Cross M, Smith E, Hoy D, Nolte S, Ackerman I, Fransen M, et al. The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(7):1323–1330. - PubMed
-
- Vos T, Barber RM, Bell B, Bertozzi-Villa A, Biryukov S, Bolliger I, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386(9995):743–800. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kiadaliri AA, Lamm CJ, de Verdier MG, Engström G, Turkiewicz A, Lohmander LS, et al. Association of knee pain and different definitions of knee osteoarthritis with health-related quality of life: a population-based cohort study in southern Sweden. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2016;14(1):1–7. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

