An Integrated Analysis of the Safety of Tofacitinib in Psoriatic Arthritis across Phase III and Long-Term Extension Studies with Comparison to Real-World Observational Data
- PMID: 32006348
- PMCID: PMC7105422
- DOI: 10.1007/s40264-020-00904-9
An Integrated Analysis of the Safety of Tofacitinib in Psoriatic Arthritis across Phase III and Long-Term Extension Studies with Comparison to Real-World Observational Data
Abstract
Introduction: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Objective: Our objective was to compare the incidence rates (IRs) of adverse events in tofacitinib clinical trials and real-world observational data for alternative treatments.
Methods: The tofacitinib "dose-comparison cohort" included months 0-12 of two phase III studies (tofacitinib 5 [n = 238] and 10 [n = 236] mg twice daily [BID]); the "all-tofacitinib comparison cohort" (n = 783) included two phase III and one ongoing long-term extension study (data cutoff May 2016). An "observational comparison cohort" (n = 5799) comprised patients initiating a conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD), biologic DMARD, or apremilast in the US Truven MarketScan database from 2010 to 2015. IRs for serious infections (SIEs; requiring hospitalization), herpes zoster (HZ), malignancies (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer [NMSC]), NMSC, and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) across cohorts were qualitatively compared.
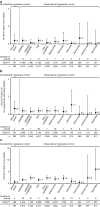
Results: IRs (patients with events/100 patient-years) for SIEs were similar between the tofacitinib dose-comparison cohort (5 mg BID: 1.3; 10 mg BID: 2.0) and the observational comparison cohort (1.1-7.9; treatment dependent). The tofacitinib dose-comparison cohort had a higher rate of HZ (5 mg BID: 2.0; 10 mg BID: 2.7) than did the observational comparison cohort (0.8-2.0). IRs for NMSC were generally lower in the all-tofacitinib comparison cohort (0.5) than in the observational comparison cohort (0.4-6.0). IRs for MACE, malignancies excluding NMSC, and NMSC were similar between cohorts.
Conclusion: In patients with PsA, tofacitinib had a safety profile similar to that of other systemic therapies in real-world settings, except for the risk of HZ, a known risk of tofacitinib.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01877668; NCT01882439; NCT01976364.
Conflict of interest statement
Gerd R. Burmester has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Gilead, Lilly, and Pfizer Inc and lecture fees from AbbVie, Lilly, and Pfizer Inc. Jeffrey R. Curtis has received research grants and consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Corrona, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Myriad, Pfizer Inc, Regeneron, Roche, and UCB. Huifeng Yun has received grant/research support from Pfizer Inc. Oliver FitzGerald has received research grants and honoraria from AbbVie, Celgene, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, and UCB. Kevin L. Winthrop has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Galapagos, Gilead, GSK, Lilly, Pfizer Inc, Roche, and UCB. Valderilio F. Azevedo has received grant/research support and consulting fees from AbbVie, Lilly, Novartis, and Pfizer Inc and lecture fees from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celltrion, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, and Pfizer Inc. William F.C. Rigby has received consulting fees for work unrelated to this manuscript. Keith S. Kanik, Cunshan Wang, Pinaki Biswas, Thomas Jones, Thijs Hendrikx, and Ricardo Rojo are shareholders and employees of Pfizer Inc. Sujatha Menon is an employee of Pfizer Inc. Niki Palmetto was an employee of Pfizer Inc at the time of the analysis.
Figures



References
-
- Coates LC, Kavanaugh A, Mease PJ, Soriano ER, Acosta-Felquer ML, Armstrong AW, et al. Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis 2015 treatment recommendations for psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(5):1060–1071. - PubMed
-
- Gossec L, Smolen JS, Ramiro S, de Wit M, Cutolo M, Dougados M, et al. European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) recommendations for the management of psoriatic arthritis with pharmacological therapies: 2015 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(3):499–510. - PubMed
-
- Gottlieb A, Korman NJ, Gordon KB, Feldman SR, Lebwohl M, Koo JY, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: Section 2. Psoriatic arthritis: overview and guidelines of care for treatment with an emphasis on the biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58(5):851–864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

